The Pithia-NRF Integration project provides access to research facilities, data collection and scientific models, and access all the possible tools the research community needs to enhance and model the understanding and modeling of the physical mechanisms that support the inter-connected regions of the Earth’s archetypes, thermospheric, and ionosphere.
Pithia-NRF (Plasma Sphere Ionosphere Thermosphere Integrated Research Environment and Access Services: A Network of Research Facility) is a European research infrastructure aimed at promoting research and development in the area of the upper atmosphere and near-geo-spatial environment. Pithia-NRF provides researchers access to testbeds for data experiments and the development of new scientific models that can be transformed as future steps, and is useful for operations that are useful for services dedicated to spatial weather monitoring and prediction and space situational awareness.


Major innovations in Pithia-nrf
1. Integrated European Research Infrastructure
Pithia-NRF establishes a comprehensive European network of experimental facilities (Phithia-NRF nodes) by integrating national and regional research infrastructure, including facilities such as EISCAT, LOFAR, IONOSONDES, Digisondes, GNSS receivers, Doppler Sound Systems, RIOMETERS, VLF receivers and more. This integration promotes coordinated observation and data sharing across Europe, and advances research into ionospheres, thermospheres, and plasma spheres.
2. Open access to data and tools
This project provides open access to data and scientific models. Through the Pithia-nrf e-science Center (ESC), researchers can access fair (easy to find, accessible, mutually repeatable, reusable) data, standardized data products, a set of data processing, forecasting tools, and workflows to drive collaborative research and innovation.
3. Standardization and interoperability
Pithia-NRF emphasizes the development of standards for interoperability of data, including data models and domain ontology. This standardization allows seamless integration of data and tools from a variety of sources and makes them available across different research platforms.
4. Transnational Access (TNA) Program
The project offers a cross-border access program that grants external researchers to use Pithia-NRF nodes. This initiative supports practical and remote projects, allowing researchers to conduct experiments, collect data and analyze results using the tools and services of the project provided by nodes and ESCs.
5. Comprehensive training and competency building
Pithia-NRF offers organizational and systematic training through workshops, schools, webinars and on-site sessions. These training programs are designed for project partners, students, scientists in countries with limited space research infrastructure, and private enterprise engineers, cultivate a skilled community of high temperature research and space science on Earth.
6. Integration with European Open Science Cloud (EOSC)
By connecting with EOSC, Pithia-NRF ensures long-term storage and accessibility of observational data. This integration supports advances in knowledge of the ionosphere, thermospheric, and plasmapheric research domains, particularly for long-term research.
Impact and future outlook
Pithia-NRF’s innovative approach in integrating diverse research infrastructures, standardizing data and tools, and promoting open access will significantly improve the capabilities of the scientific community, researching and understanding the upper atmosphere and the spatial environment near the Earth.
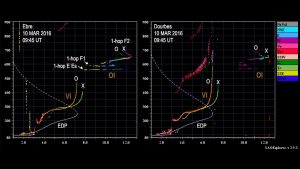
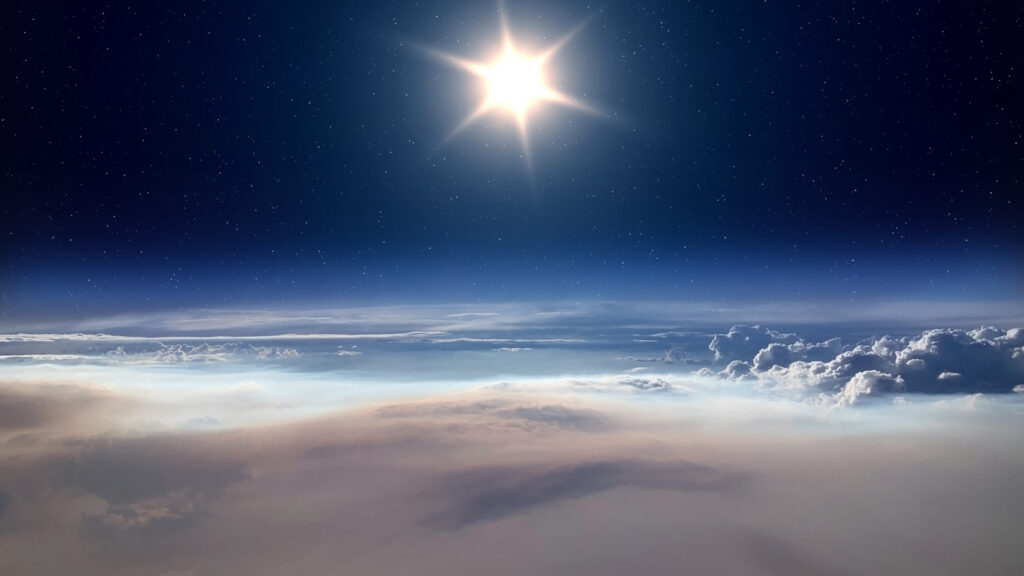
By promoting collaborative research and providing comprehensive training, this project not only advances current scientific knowledge, but also lays the foundation for future innovations in space meteorological research and related technologies. The TNA project implemented on the Pithia-NRF node includes multi-character data analysis, development and verification of scientific models, media imaging methods during ionosphere intervention intervention intervention, and calibration of new instruments, and Belehaki et al. (2025) demonstrated research advances in the calibration of new equipment in an article published by (2025).
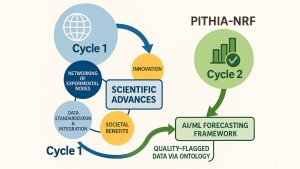
Based on these successful developments, Pithia-NRF could have a significant impact on building a scientific community, generating innovation, providing social benefits, and influencing future governance and funding decisions. The main achievements that promote all impacts come from scientific advancements.
However, a major additional benefit in particular the operational domain is the possibility that Pithia-NRF ontology will characterize data products with quality flags. This can meet the requirements of the Space Safety and Security Program of the European Space Agency and the European Union Space Program. This requires controllable quality data. This is a very complex procedure that requires cleaning, curation, transformation and integration of other workflows, and is planned for the Pithia-NRF community to achieve with its follow-up project. Such developments will greatly support future AI/ML modeling developments where clean data and availability of archived data will help to ensure model performance and reliability of retraining processes, along with the availability of tools for acquiring large-scale archived data.
Establishing an AI/ML modeling framework is the next major goal of the Pithia-NRF community and to address the key requirements for real-time prediction with specified accuracy for plasma ball mechanics that rely on geomagnetic disturbances and irregularities, atmospheric drag effects, and geomagnetic activity.
reference
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2024.11.065
Source link

