SDGS-Eyes will turn satellite data into smart tools to boost Europe’s progress on sustainability goals.
The SDG-S Eyes project (Sustainable Development Goals – Enhanced surveillance by the Copernicus Services family) is the Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Action (RIA), designed to enhance Europe’s ability to monitor SDGs using Copernicus data. By developing a portfolio of decision support tools for monitoring SDG indicators, SDGS-Eyes aligns with EU green trading priorities, promoting an intersector approach to sustainability monitoring and directly supporting climate change targets with satellite-driven solutions.
Seven services have been developed under SDGS-Eyes Umbrella, demonstrating how their methodologies and tools can enhance the reporting of SDG 13 (climate behavior), SDG 14 (life under water), and SDG 15 (Life on Land). The SDGS-Eyes service is co-designed with the National Statistics Office, Environmental Agency and Forest Managers, which connects researchers and community experts with a wide range of stakeholder communities.
SDGS-Eyes operates within a framework established by the United Nations and the National Statistical System for SDG monitoring.
Vision in operation
To translate its comprehensive ambitions into tangible results, SDGS-Eyes focuses on mutually linked objectives.
Improved access and ease of use of Earth observation data
SDGS-Eyes has built a scientific and technical framework to generate robust and accurate data for monitoring indicators. By aggregating and processing data from Copernicus’ six core services, together with space-based and in-situ sources, the project makes Earth Observation (EO) data more accessible, easy to use and feasible. Improved SDG indicator quality
This project presents seven indicators of Copernicus reinforcement measurements across three SDG targets (SDGS 13, 14, and 15). Build stakeholder capabilities for social impact
To maximize relevance and ease of use, SDGS-Eyes offers service-oriented data products co-designed with end users, such as public institutions, researchers, and environmental institutions. This collaborative approach makes the tool fit the purpose of actual decision-making and reporting contexts.
These objectives converge to realize the comprehensive ambitions of the project. This is to develop user-friendly, accurate and efficient tools that enhance monitoring, reporting and use of SDG indicators across Europe.
Building Blocks: SDGS-Eyes Framework
SDGS-Eyes has brought together research and industry experts along with stakeholders from various communities to collaborate on scientific, technical and user engagement frameworks to monitor SDGS indicators.
The sdgs-eyes methods and tools are designed as follows:
User Driven – Over a series of workshops and consultations, end users provided feedback to ensure maximum ingestion and impact in methodological design. Scientific Driven – Collecting already existing data and enriching them using EO and other sources from Copernicus leads to a healthy scientific and technical framework, enhancing indicator monitoring and reporting.
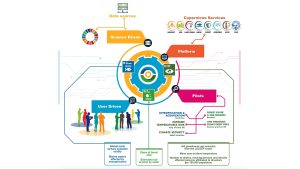
The structure of the SDGS-Eyes project is provided in Figure 1, and can be summarized into the following major components:
Data Integration Platform – A platform for aggregation and processing of multiple EO data sources, including satellites, in situ, numerical models, and data analysis. Pilot Demonstration – Five pilot projects have been implemented to demonstrate, evaluate and evaluate services developed in real-world contexts.
Platform
The platform is cloud-based, cost-effective, has an intuitive interface that also provides access to small administrators. It typically provides a faster and potentially reliable alternative to traditional national inventory, which reports SDGS indicators annually.
pilot
The SDGS-Eyes solution has been demonstrated through four EUs and one non-EU pilot area. The pilot location is shown in Figure 2.
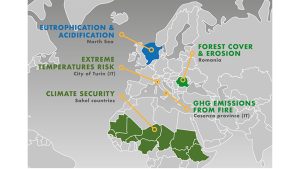
Pilot 1 – Greenhouse gas (GHGS) emissions from forest fires
The pilot will proceed with SDG monitoring, reporting and accounting for GHGS emissions caused by forest fires. Capitalize Copernicus’ combustion region, biomass and Scorch-Height products to generate high-precision emissions maps that support SDG 13 reports, along with in-situ calibration data. This underscores the importance of close cooperation between research institutions, national statistics offices, forestry experts, private companies and policymakers to improve GHGS emission tracking across the EU.
Pilot 2 – Extreme temperature risks in urban areas
The pilot will focus on urban heat insurance nexus and develop a Copernicus-based tool that maps climate risks along with demographic, socioeconomic, health and built environmental data. The integrated risk assessment informs planning and response strategies for urban extreme temperature events that directly support SDG 13’s resilience efforts.
Pilot 3 – Eutrophication and acidification of the North Sea
Focusing on marine SDGs, the pilot will leverage Copernicus’ marine services dataset and satellite, in situ and model outputs to generate high-resolution maps of seawater acidity and nutrition-driven nutrients. The resulting indicators strengthen policies that guide SDG 14 monitoring, coastal eutrophication, acidification hotspots and sustainable marine resource management.
Pilot 4 – Forest Covering and Erosion
The pilot uses Time Series Sentinel Images and Machine Learning Classifiers to quantify forest cover dynamics and identify soil erosion risk zones. Enhance SDG 15 indicators of ground ecosystem health and land use sustainability by automating detection of deforestation, degradation and erosion hotspots.
Pilot 5 – Climate Security in the Sahel
The pilot focuses on assessing the impact of disasters, including buildings and communities affected by the Sahel region (part of sub-Saharan Africa) to support climate safety and disaster resilience. These datasets provide SDG 13.1.1 (“Assisted Per 100,000”) and inform the resilience and security policy of vulnerable Sahel populations.
Practical Insights: SDGSEYES Service Framework
The SDGS-Eyes project has developed an advanced set of Earth observation-driven services designed to enhance monitoring and reporting of specific SDG indicators across climate, marine, and terrestrial domains.
Greenhouse gas emissions from forest fires (EFF)
The service automates near-real-time estimation of GHGS emissions (Co2, Ch₄, etc.) from forest fires. Calibrate in situ data using Copernicus’ combustion regions, biomass, and burnt-height products to generate high-resolution emission maps. This will advance national reporting based on IPCC and UNFCCC¹ guidelines and enhance EU-wide data compiled by the European Environment Agency.
Target indicators: EU SDG Indicator 13.21, “Net Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Land Use, Land Use Changes and Forestry (LULUCF) Sector” and UN Indicator 13.2.2, “Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions.”
2. Urban Heat Insurance Nexus Risk (HHR)
The service integrates climate risk metrics (temperature, humidity, precipitation), demographics, socioeconomic, health, and built-up environmental data into Copernicus-based tools. The result is a high-resolution risk map that supports adaptation strategies focused on urban resilience and health.
Target Indicator: Advances the old EU SDG indicator “average ground temperature deviation” by developing a comprehensive thermal health risk indicator.
3. Affected Buildings and People (ABP)
This innovative EO-based service quantifies the impact of disasters such as damaged structures and affected groups following Sahel floods and extreme events. This bridges the key data gaps supporting resilience policies in vulnerable regions by converting EO data into humanitarian metrics.
Target Indicator: UN 13.1.1 ‘Deaths, Missing Persons, People who are directly affected per 100,000 people.”
4. Sea surface acidity (SSA)
Using Copernicus Marine Service data and satellites and in situ systems, this indicator tracks pH levels in the North Sea. This allows monitoring of marine acidification trends, which are important for the conservation of marine ecosystems.
Target Indicator: The EU definition, “Global Average Sea Water Surface Acidity,” reflects UN Indicator 14.3.1, “Mean Ocean Acidity (PH) measured in an agreed suite of representative sampling stations.”
5. Seawater eutrophication
The service uses remote sensing and marine models to map coastal eutrophic areas within the EU’s exclusive economic zone (EEZ). Products include the total area (km²) and percentage (%) of eutrophic water to inform the health strategies of marine ecosystems.
Target Indicator: Based on the EU definition, “seawater affected by eutrophication” also reflects UN Indicator 14.1.1(a) “Indicator of Coastal Eutrophication.”
6. Changes in forest cover (FCC)
By leveraging high-resolution Sentinel imagery and change detection algorithms, the service identifies changes in forest cover, not only forest extent, but also forest cover, such as deforestation, planting, and degradation hotspots.
Target Indicator: Remembering the EU definition of “forest zone share” and also UN Indicator 15.1.1 “as part of the total forest area area.”
7. Soil erosion by water (sewing)
Using satellite data, topographical models, and hydrological analyses, the service maps areas affected by severe water-driven soil erosion. This provides a broader assessment of land degradation and sustainable land management policies.
Target Indicator – Remembering the definition of the EU, “Estimated Soil Erosion by Water – Areas affected by severe erosion rates”, UN Indicator 15.3.1, “Percentage of Land Degraded to Total Land.”
Key takeout
A joint design approach
The SDGS-Eyes service is developed through a sustainable co-design process to directly address the needs of end users, including national statistics offices, environmental agencies and forest managers. Regular workshops and webinars allowed integration of user feedback and ensured integration between existing monitoring frameworks and reporting standards.
EO Data Integration
The project leverages Copernicus Core Services EO data in combination with an in situ source to provide accurate and timely SDG indicator monitoring data. It focuses on six enhanced indicators across three interconnected SDGs (SDG13 (climate behavior), SDG14 (living under water), and SDG15 (land life)) as well as cross-cut indicators that assess exposure to extreme climate events in vulnerable communities. The key output is the SDGS-Eyes platform, which provides analytics-enabled datasets and tailored tools for a wide range of stakeholders.
Stakeholder engagement
The active involvement of policymakers, researchers, public institutions and private sector actors is central to pilot design and implementation. Their involvement makes the service practical, influential and ready for real-world applications.
Capacity Building
By promoting long-term data reliability and supporting user capabilities, SDGS-Eyes helps lay the foundation for the broad adoption of EO-based solutions in SDG monitoring, promoting lasting impacts well beyond the duration of the project.
This article also appears in Space Special Focus Publication.
Source link

