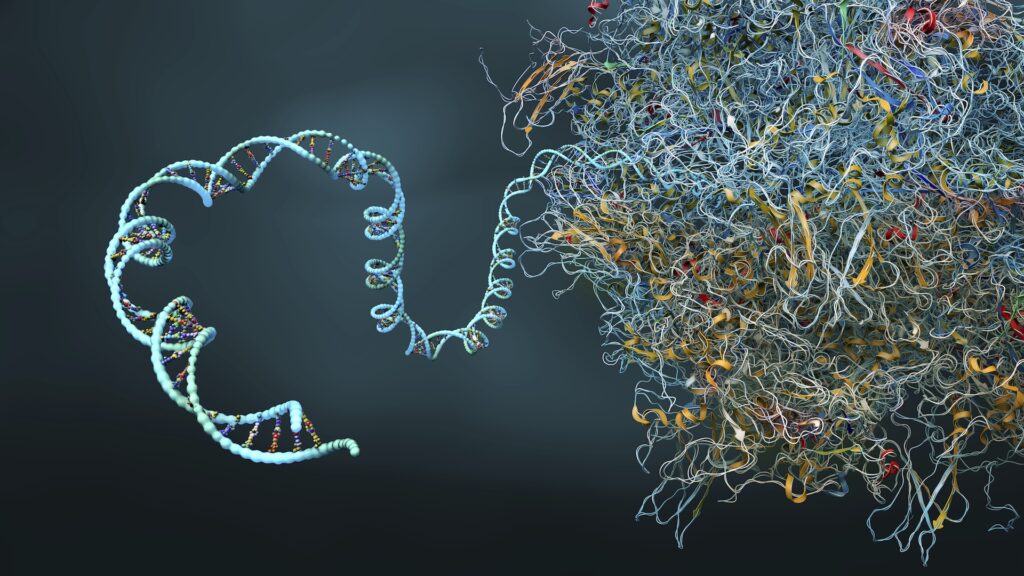
Researchers at IBM and Moderna have used quantum simulation algorithms to predict the complex secondary protein structure of the longest 60 nucleotide long mRNA sequence ever simulated on a quantum computer.
Messenger ribonucleic acids (mRNAs) are molecules that carry genetic information from DNA to ribosomes. It is used to create effective vaccines that can direct cell protein synthesis and incite specific immune responses.
It is widely believed that all the information required for a protein to adopt the correct three-dimensional conformation is provided by its amino acid sequence or “folding”.
You might like it
Although it is composed solely of a single strand of amino acids, mRNAs have a secondary protein structure consisting of a series of folds that provide a specific 3D shape for a particular molecule. The number of possible folding permutations increases exponentially with each nucleotide added. This creates the challenge of predicting mRNA molecules at a higher scale and easier to handle.
The IBM and Moderna experiments were reviewed in a study first published in the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering, demonstrating how quantum computing can be used to enhance traditional methods for making such predictions. Traditionally, these predictions have typically relied on binary, classic computers, and artificial intelligence (AI) models such as Google Deepmind’s Alphafold.
Related: DeepMind’s AI program Alphafold3 can predict the structure of all proteins in the universe and show how they work
According to a new study published May 9 in the Preprint ARXIV database, algorithms that can be performed on these classic architectures can process mRNA sequences with “hundreds or thousands of nucleotides,” but only by excluding higher complexity features such as “fake knots.”
Pseudo knots are the complex torsions and shapes of the secondary structure of molecules that can have more complex internal interactions than regular folds. Through their exclusion, the potential accuracy of protein folding prediction models is fundamentally limited.
Understanding and predicting the minimal details of the protein fold of mRNA molecules is inherent to developing stronger predictions and, consequently, more effective mRNA-based vaccines.
Scientists hope to overcome the limitations inherent to the most powerful supercomputers and AI models by augmenting experiments using quantum technology. Researchers conducted multiple experiments using quantum simulation algorithms that rely on quantum equivalents to computer bits to model molecules.
First, using only 80 qubits (80 of the 156 possible) on the R2 Heron quantum processing unit (QPU), the team adopted a conditional risk-based mutational Quantum algorithm (CVAR-based VQA) with a 60 nucleotide-long mRNA sequence.
Research shows that the previous best of quantum-based simulation models was a 42-nucleotide sequence. The researchers also expanded their experiments by applying recent error correction techniques to address noise generated by quantum functions.
In a new preprint study, the team tentatively demonstrated the effectiveness of the experimental paradigm in running simulated instances with up to 156 qubits for mRNA sequences of up to 60 nucleotides. They also conducted a preliminary study showing the possibility of using up to 354 qubits for the same algorithm in a noiseless setting.
Ostensibly, increasing the number of qubits used to execute the algorithm should result in scaling the algorithms for additional subroutines to lead to more accurate simulations and the ability to predict longer sequences.
However, they said, “These methods require the development of advanced technologies to embed these problem-specific circuits into existing quantum hardware.”
Source link