It has been discovered that popular password manager plugin web browsers could click on security vulnerabilities that could be exploited to steal account eligibility, two-factor authentication (2FA) codes and credit card details under certain conditions.
The technique dubbed a Document Object Model (DOM)-based extension by independent security researcher Marek Tóth, who published his findings at the DEF CON 33 Security Conference earlier this month.
“Attackers can now steal user data (credit card details, personal data, and login credentials including TOTP) anywhere on attacker-controlled websites,” Tóth said. “The new techniques are common and can be applied to other types of extensions.”

ClickJacking, also known as UI Redressing, refers to the type of attack in which a user is tricked into performing a series of actions on a website that appears to be harmless on the surface, such as by inadvertently performing an attacker’s bid, such as by clicking a button.
A new technique detailed by Tóth involves manipulating UI elements on web pages that inject browser extensions into the DOM, essentially using malicious scripts.
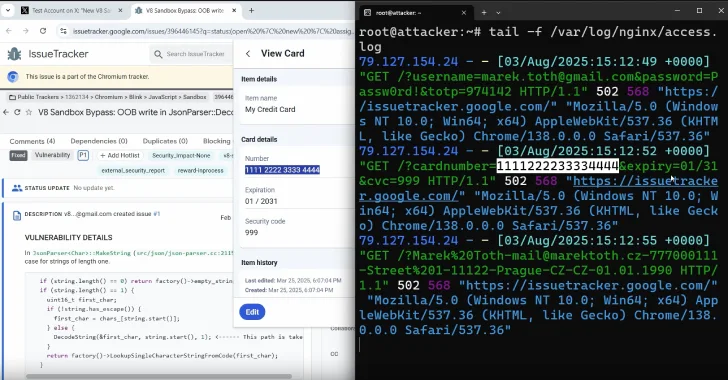
The study focuses specifically on 11 popular password manager browser add-ons ranging from 1 password to iCloud passwords, all of which were susceptible to DOM-based extension clickjacking. Collectively, these extensions have millions of users.

To stop attacks, all bad actors have to do is create fake sites with intrusive pop-ups like login screens and cookie consent banners, but also embed an invisible login form and click on the site to close the pop-up, so the password manager automates the credentials and excludes them on the remote server.
“All password managers met their credentials not only in the “main” domain, but also in all subdomains,” explained Tóth. “Attackers can easily spot XSS or other vulnerabilities and steal a user’s saved credentials with a single click (10 out of 11) including TOTP (9 out of 11). Passkey authentication could also be exploited in some scenarios.”

Following responsible disclosure, six vendors have not yet released fixes for the defects –
1Password Password Manager 8.11.4.27 Apple Icloud Passwords 3.1.25 Bitwarden Password Manager 2025.7.0 Enpass 6.11.6 LastPass 4.146.3 Logmeonce 7.12.4

Software supply chain security company Socket, which independently reviewed the survey, said that Bitwarden, Enpass and iCloud passwords are actively working on fixing, with 1Password and LastPass markings useful. We are also contacting US-Cert to assign the CVE identifier for the identified issue.
Until the fix is available, users are advised to disable the password manager’s autofill feature and use copy/paste only.
“For Chromium-based browser users, use the extended settings[オン]Click[オン]”We recommend configuring site access to the site,” Tóth said. “This configuration allows users to manually control the autofill feature.”
Source link