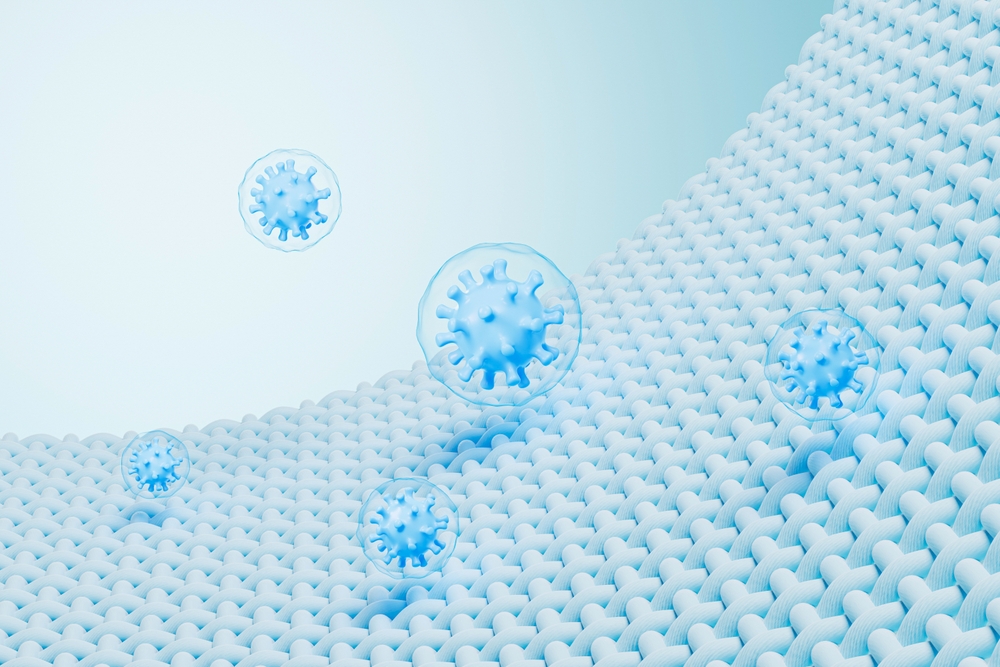
The antibacterial coating acts as an invisible shield and provides a protective barrier against harmful microorganisms.
These advanced materials are formulated to inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses on a variety of surfaces.
Utilizing a variety of active agents such as silver ions and copper compounds, these coatings disrupt microbial cell functions, thereby preventing replication and survival.
The effectiveness of antibacterial coatings is often measured by their ability to reduce microbial loads on surfaces, resulting in a significant reduction in the risk of contamination.
Additionally, these coatings can be applied to a variety of materials, such as plastics, metals, and textiles, enhancing safety in both public and private settings.
The science behind these coatings is rooted in nanotechnology, allowing precise manipulation at the molecular level to maximize antibacterial effects.
As a result, antibacterial coatings not only contribute to improved hygiene, but also promote overall public health by reducing spread spread of infectious diseases in a variety of environments.
Transforming infection control in health care
As healthcare facilities increasingly prioritize patient safety, the implementation of advanced antibacterial coatings is revolutionizing infection control practices.
These coatings are designed to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria on the surface, significantly reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
By applying these innovative materials to high-touch areas such as bed rails, surgical instruments and waiting room furniture, hospitals create an environment that encourages microbial growth.
Studies have shown that surfaces treated with antibacterial coatings exhibit a significant reduction in bacterial load, which is important in protecting vulnerable patients.
Additionally, these coatings are durable and require minimal maintenance, ensuring long-term protection without frequent reapplications.
Hospitals employing these technologies not only enhance patient outcomes, but also reduce healthcare costs associated with long-term hospital stays and additional treatment for infectious diseases.
Protect public spaces from pathogens
Public spaces are essential for community interaction, but often act as hotspots for pathogen transmission, pose a great risk to public health.
High-touch surfaces such as doorknobs, handrails and elevator buttons are particularly vulnerable as they promote the spread of bacteria and viruses among individuals.
Increased walking paths in these areas amplify the potential for transmission and make effective hygiene important.
To mitigate these risks, the implementation of antibacterial coatings at these touchpoints has emerged as a promising solution.
In public places, integrating such technologies not only enhances hygiene, but also promotes public trust in safety measures.
As communities continue to navigate health challenges, protecting touchpoints through innovative coatings represents a proactive approach to protecting public health.
Emerging materials and technologies in antibacterial innovation
Materials and technology innovations are driving advances in antibacterial solutions and offering new avenues to enhance public health.
Recent developments include the use of nanomaterials such as silver nanoparticles and graphene, which exhibit strong antibacterial properties while minimizing toxicity to human cells.
These materials can be incorporated into coatings on a variety of surfaces, including medical devices and public infrastructure, effectively reducing the risk of infection.
Additionally, researchers are exploring bio-inspired materials that mimic natural antibacterial mechanisms found in shark skin. These innovations not only increase the effectiveness of the coating, but also promote lifespan and durability in high traffic environments.
Furthermore, advances in smart technology allow for the integration of reactive antibacterial surfaces that activate when contacted with pathogens, providing a proactive approach to infection control.
Collectively, these new materials and technologies represent a major leap in the ongoing battle against harmful microorganisms in public places.
Public health has a massive impact
How can cities leverage advances in antibacterial coatings to enhance public health on a larger scale?
Integrating these innovative materials into urban infrastructure provides transformative opportunities to reduce spread spread of infectious diseases.
By applying antibacterial coatings to high-touch surfaces such as public transport, hospitals, and schools, cities can create environments that actively hinder bacteria growth.
This aggressive approach not only protects vulnerable groups, but also reduces the burden on the health care system.
Furthermore, these coatings may contribute to improved air quality and reduced overall maintenance costs by minimizing the need for frequent cleaning.
The cumulative effects of widespread implementation promote a culture of health-conscious living and encourage residents to engage in the community space more freely.
Ultimately, the adoption of antibacterial coatings demonstrates a commitment to public health, paving the way for healthier cities and a safer future, significantly reducing the risk of disease transmission.
Safety, regulations and the road ahead
When cities try to implement antibacterial coatings on a large scale, they face serious safety and regulations-related challenges. The effectiveness and safety of these coatings should be assessed thoroughly to avoid pose health risks to the general or the environment.
Regulators such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are responsible for overseeing these products, but the rapid pace of innovation often outweighs the development of comprehensive guidelines.
Furthermore, there are concerns regarding the potential development of bacterial resistance that may impair the effectiveness of these coatings. Transparency in the composition and application of these products is essential to public trust.
As urban areas move forward, collaboration between scientists, manufacturers and regulatory agencies is critical to navigate these challenges and promote the responsible adoption of antibacterial coatings.
Antibacterial coatings represent significant advances in public health and provide effective solutions to reduce pathogen transmission in a variety of environments. By converting high-touch surfaces into a safer space, these coatings promote hygiene and enhance public opinion.
As new materials and technologies emerge, the potential impact on healthcare and urban environments continues to grow. However, addressing regulatory challenges and ensuring widespread adoption remains important to maximize its benefits, ultimately contributing to healthier cities and safer communities for all.
Source link