Large companies are getting smaller and CEOs want everyone to know about it. Wells Fargo has cut its workforce by 23% in five years, Bank of America has taken 88,000 employees since 2010, and Verizon CEO has recently boasted that its staff is “always down.” What once was a sign of corporate distress has become a badge of honor to celebrate lean operations and AI-driven efficiency.
However, while C-Suite leaders advertise that they will “do more,” CISOs have fewer resources, but all preventable security incidents are exponentially expensive. Security teams are already growing thin and thin, and as developer-to-security ratios reach unsustainable levels, these workforce cuts have pushed out the breaking point for already-struggling teams. Against the backdrop of workforce optimization, hard-coded secrets represent particularly dangerous blind spots that cannot be managed through manual processes or reactive firefighting.
Numbers don’t lie
The qualification crisis is already here. According to the latest IBM investigation, 86% of violations include stolen or breached credentials, extending the average time to identify and contain these cases for 292 days.
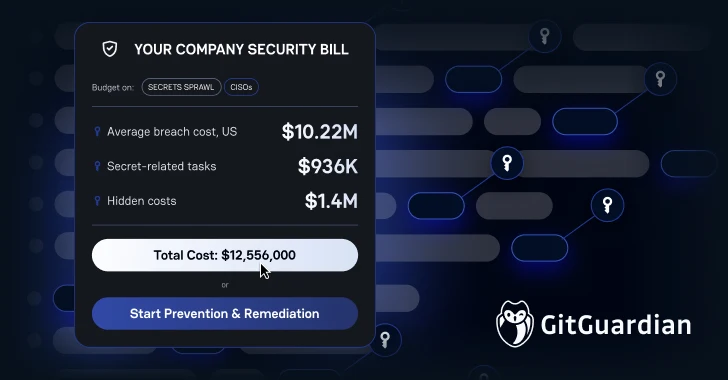
Financial interests are higher than ever. In the US, breach costs have skyrocketed to an all-time high of $10.22 million due to regulatory fines and increased detection costs. Especially for qualification-based incidents, Hasicorp research shows that these violations have a $750,000 premium. That is, US organizations face potential costs of over $11 million when hard-coded secrets are involved.
However, hidden costs may be even more devastating. Organizations waste around $1.4 million a year by manually managing secrets. This includes developers spent on qualification rotation and exposure investigations ($936,000) and security analysts triage false positives and chasing leaked credentials (>$500,000).
Real world influences are already shown. Canva has experienced days of downtime with multiple teams due to one leaked secret that consumed engineering resources that should have focused on product development.
Why Lean Teams Amplify Risk
A reduction in the workforce means longer average time compensation cases, making the average 292-day average containment window even more dangerous. Each security incident separates already stretched teams from their core business functions, creating costly context switching overheads that lean organizations cannot afford.
Even as teams shrink, the scope of the problem continues to expand. Large organizations have thousands of unmanaged secrets scattered across code repositories, CI/CD pipelines, slack channels, JIRA tickets, and collaboration platforms.
Hashicorp’s research shows that up to 40% of these secrets fall into high-risk categories and often provide direct production access.
This creates a multiplication effect. Hard-coded API keys allow for lateral movement, supply chain compromises, and large-scale ransomware deployment. The recent S1ngularity attacks demonstrate this perfectly. The GithubActionAction Token-Stealing Pull Request started as a compromised NX package, cascaded it to attackers who exposed 82,901 additional secrets by stealing 2,349 qualifications and publishing over 10,000 private repositories.
Strategic response: Accuracy beyond volume
Gitguardian’s approach to secret security recognizes the fundamental truth. Detection alone is not enough. Without effective repairs, alerts are already expensive noise that overwhelms your team. This distinction is important for CISOS, which manages learner security operations.
Secrets present a fundamentally different challenge from traditional vulnerabilities. Developers can usually patch code vulnerabilities independently, but improving exposed secrets requires understanding of the broader infrastructure context. You need to understand that secrets are used across multiple services, relying on the system, and who has the authority to rotate them. This often requires coordination between development, platforms, and DevOps teams, each with its own priorities and workflows. Collecting this context allows for manual collection of this context to change what needs to be quickly rectified for complex multi-team investigations that grow for weeks, if your security team is already operating at capacity.
Advanced platforms now shift their focus from “what’s exposed.” By providing contextual information including roles, permissions, ownership and threat scope in “What is the size of the exposure?” This overall approach directly addresses the false positive burden that costs an organization that costs more than $500,000 a year on wasted analyst time.
Reduce repair times from week to time
An effective repair framework matches perfectly with the constraints of a lean team.
Proactive detection: Platforms implementing both preventive scans and reactive scans of existing leaks during commits capture the problem before reaching the 292-day average containment window.
Clear Ownership: Instead of broadcasting ambiguous alerts, modern tools assign ownership to all secrets, ensuring that responsible developers receive notifications in full context. This will waste time hunting secret owners.
Informational Decision Making: Teams receive accurate location data, understand what each secret will be unlocked, and know if it is still active. According to the Hashicorp research above, this targeted approach prevents $936,000 in productivity drainage from manual investigation tasks.
Workflow integration: Developers get clear repair guidance directly within existing tools, reducing the cost of switching contexts that bothers small teams. Advanced platforms provide automated secret revocation capabilities, allowing developers to directly generate code-fixed pull requests within version control systems, allowing developers to come across exactly where they work, rather than forcing them to individual security tools.
Smart Repair ROI
By identifying specific files and lines of code where secrets are hardcoded, Gitguardian’s approach translates the economics of incident response. Instead of spending hours searching for a developer’s codebase, focus their efforts exactly where they need them. Real-time remediation tracking provides visibility without having to monitor manually.
This precision approach directly addresses the core challenges faced by downsized security teams.
Source link