AvantGuard’s AVA-003 compounds provide an aggressive solution to antimicrobial resistance, targeting pathogens with sustained activity, and addressing the urgent need for innovative infection prevention in medical and conflict zones.
The global antibacterial resistance (AMR) crisis, exacerbated by overuse of antibiotics and slow drug development, has created an urgent need for alternative infection prevention strategies as multidrug resistant pathogens grow in healthcare environments and competitive zones like Ukraine. AvantGuard’s new antiseptic compound, called AVA-003, provides active infection prevention through sustained antibacterial activity. Unlike traditional antibiotics, AVA-003 exhibits comparable activity against antibiotic-sensitive resistant bacteria/fungals via selective microbial cell wall targeting. This broad non-specific mechanism allows for immediate decolonization in wound beds, while preventing the development of wound resistance. AVA-003 represents a paradigm shift from reactive treatment to aggressive prevention, providing essential resistance tools to manage the post-antibiotic era.
Modern wound treatment challenges
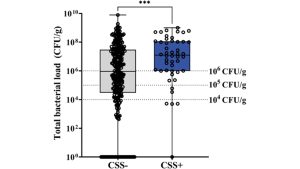
Imagine you are a doctor, and the patient presents with a mild cut after swimming in the ocean. Pass the standard clinical signs and symptoms checklist (CSS) and decide not to prescribe antibiotics. Unfortunately, CSS consistently underestimates the amount of bacteria in the wound (Figure 1), and since the patient is back with mildly infected wounds, prescribing first-line antibiotics such as doxycycline, which indicates saline wound treatment. A week has passed and the treatment is not working. Your patient’s wounds are big. Order culture and resistance tests to treat appropriately. This test may take up to 3 days. By then, the pathogens had spread to immunocompromised patients within the patient community and hospital system. It turns out that pathogens may or may not be highly susceptible to the effects of other antibiotics. Perhaps even worse, there are two multidrug resistant strains, each of which is susceptible to different antibiotics. As the situation and the patient get worse, time is no longer on your side.
Global AMR crisis
We are losing the war between bacteria and fungi
Antibiotic resistance is being accelerated by overuse and misuse of standard antibiotics, misused by inadequate hygiene and inadequate infection control, and is becoming rapidly becoming one of the most pressing global health threats. According to the World Health Organization, at least 1.27 million people die each year from drug-resistant infections, and this number is expected to increase dramatically if the current trend continues. 2This crisis is exacerbated by the surprisingly slow development of new antibiotics. Preferred pathogens are bacteria identified by health groups as pose the greatest threat because they developed resistance to multiple antibiotics. Similarly, multidrug resistant pathogens are organisms that cannot be treated with some commonly used antibiotics, significantly limiting treatment options. As resistivity increases and effective treatments decrease, health care systems around the world face the harsh reality that they cannot contain or treat the spread of these dangerous infectious diseases.
Healthcare providers are currently facing impossible choices. When first-line antibiotics fail against these multidrug-resistant pathogens (organisms that shrugged several commonly used drugs), clinicians must escalate to the final resort treatment, which often complicates complex side effects. Each time you use these powerful weapons, there is more resistance and accelerates a very crisis intended to deal with. The broad dependence on broad spectral antibiotics underscores the urgent need for alternative strategies to control resistant pathogens.
Ukraine has become zero ground in the future after antibiotics
Battle-related heavy metal poisoning is a potential contributor to further strengthen antibacterial resistance between bacterial populations. 3 In addition to this, deep challenges in maintaining soldier hygiene and an increase in untreated injuries amid ongoing conflict.
Healthcare providers in these environments face formidable obstacles due to limited resources to identify resistance patterns, maintain hygiene protocols, and access to appropriate antibiotics. Not only does pathogens spread within hospitals, they can also lead to systemic infections that are difficult to create and eradicate biofilms in medical devices and wounds.
Specific examples emphasize the gravity of the situation. For example, the pan-resistant strain of cleviciera pneumonia is isolated from wounds in Ukrainian soldiers. These highly toxic strains have been documented in US military hospitals in Europe treating Ukrainian patients, highlighting the global scope of the issue.
The post-antibiotic world is already here. These developments demonstrate the urgent need for effective alternative infection prevention strategies as traditional antibiotics become increasingly unreliable in the face of rapidly evolving resistance.
Prevention is the best treatment
Preservatives offer alternative strategies for antibiotics and attack pathogens through a wide range of mechanisms that bacteria cannot facilitate resistance. Rather than targeting a single bacterial process, it disrupts multiple critical systems at once, making it much more difficult for organisms to adapt and survive.
However, the actual limitations of current preservatives cannot be overlooked. For example, drugs such as chlorhexidine and iodine are widely used in clinical and surgical environments to disinfect skin, wounds and medical devices due to their strong antibacterial properties. However, their effectiveness is costly: excessive use or application on sensitive tissue can cause skin irritation and delayed healing.
AVA-003: Breaking the cycle of resistance
AvantGuard designed a paradigm shift in infection control
AVA-003 represents the first preservative to resolve the fundamental trade-offs that have been worrisome to prevent infection for decades. It’s an efficacy and safety choice. Available as both liquid and hydrogels, this groundbreaking formulation offers unprecedented antibacterial activity compared to all other preservatives and topically applied antibiotics.
Data tells a compelling story
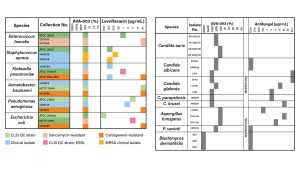
While traditional antibiotics and antifungal properties show very inconsistent results for different pathogens (Figures 2 and 3), AVA-003 exhibits uniform lethality. Resistant or susceptible to bacteria or fungi – no difference. AVA-003 kills all efficacy equally and eliminates speculation that made empirical therapy a patient’s life and gamble.
Uncompromising safety
The selective targeting mechanism of AVA-003 preferentially attacks microbial cell walls rather than human tissue. This accuracy allows for a wide range of applications for the same compounds: surface sanitization, sterilization of surgical instruments, and treating wounds without fear of tissue damage or delayed healing. The result is a single agent that can disinfect the entire healthcare environment while being generous enough to direct patient application.
Consider a clinical transformation
That same patient presents with contaminated marine wounds, but instead of the familiar cascade, it underestimates the bacterial load, prescribes antibiotics, develops resistance, escalates treatment, and spreads resistant pathogens. The wounds are healed cleanly. No resistance occurs. No follow-up visits are required. Communities remain safe and healthcare resources are preserved for a real emergency.
In the battle zone, AVA-003 is the multiplier of force
Field Medic can neutralize dangerous pathogens at the time of injury and prevent the transport of resistant organisms to military hospitals. Those that once sown with the pan-resistant bacteria epidemic are contained in the source, protecting both individual soldiers and the entire health care system.
This is more than a progressive improvement – it’s a rethink of infection prevention

As pandemics of pandemics and fungi run towards a post-antibiotic future where global health security threaten, AVA-003 offers only a sustainable path. The future of infection control is not about finding new ways to kill super bugs. That’s to ensure that they don’t appear at all.
reference
Serena, TE; Gould, L. ; Osey, K. Kirsner, reliance on RS clinical signs and symptoms assessment leads to the misuse of antibiotics: post hoc analysis of 350 chronic wounds. Advances in Wound Care 2021, 11 (12), 639–649. doi: 10.1089/cund.2021.0146 (Accessed 2025/09/10). Murray, CJL; Ikta, KS; Sharara, F. ; Swetschinski, L. ; Robles Aguilar, G. ;Grey, A. ;Han, C. ; Bisignano, C. ;Rao, P. ;Wool, E. ; et al. Global burden of bacterial antibacterial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399 (10325), 629–655. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736 (21) 02724-0 (accessed September 10, 2025). Balta, I. ;Lemon, J. ;Gaddhaji, A. ; Cretescu, I. ; Stef, D. ;Pet, I. ; Stef, L. ; McCleery, D. ;Douglas, A. ; Corcioinoschi, N. Interaction with antimicrobial resistance, heavy metal contamination, and the role of microplastics. Front Microbiol 2025, 16, 1550587. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1550587 from NLM. Ljungquist, O. ;Magda, M. Giske, CG; Terra Pragada, C. ; Nazarchuk, O. ; Dmytriiev, D. ; Thofte, O. ; Öhnström, V. ; Matuschek, E. ;Brom, am; et al. Resistant pneumonia surgery, isolated from victims of the Ukrainian war, is highly toxic. J Infect 2024, 89 (6), 106312. doi: from 10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106312 to NLM. King, D. ; Huang, X. ;LV, W. ;Zhou, J. Povidone-Iodine Irrigation in Fracture Surgery. Toxicity and Antibacterial Effects. Orthop Surg 2022, 14(9), 2286–2297. doi: 10.1111/os.13422 From NLM. Fiorillo, L. ; D’Amico, C. ; Mehta, V. ; Cicciù, M. ; Cervino, G. Chlorhexidine Cytotoxicity in Oral Behavior: A Systematic Review of the Last 20 Years. Oral Oncology Report 2024, 9, 100245. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oor.2024.100245.
This article will also be featured in the 24th edition of Quarterly Publishing.
Source link