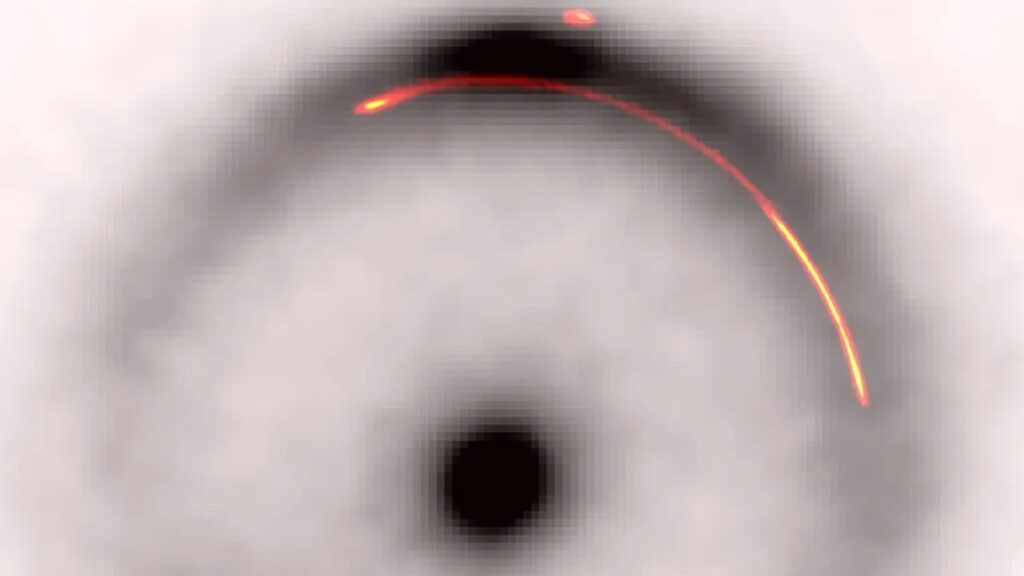
Astronomers have discovered a surprisingly small “dark object” lurking in a distant, distorted ring of light. This record-breaking discovery could help unravel the mysterious nature of dark matter, which will have a major impact on the field of cosmology.
The hidden object, possibly an invisible mass of dark matter, was discovered inside B1938+666, an “Einstein ring” located about 10 billion light-years from Earth. This bright halo (which appears dark in the black-and-white image) is made up of light from distant galaxies bent around the closer foreground galaxy (the dark dot at the center of the ring). This is the effect of gravitational lensing, a phenomenon first proposed by Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity in 1915.
you may like
B1938+666 was discovered in the 1990s. But in two new studies published October 9 in the journals Nature Astronomy and Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, researchers took a closer look at objects affected by gravitational lensing and found subtle wobbles in the pronounced arc of radio waves in the outer ring (colored red and yellow in the image). They quickly realized that this was a gravitational disturbance caused by a hidden object.
“From the first high-resolution images, we immediately observed a narrowing of the gravitational arc, a clear sign that we are on top of something,” John McKean, an astronomer at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands and the University of Pretoria in South Africa, and co-author of both new studies, said in a statement. “Only a small clump of mass between us and a distant radio galaxy could cause this.”
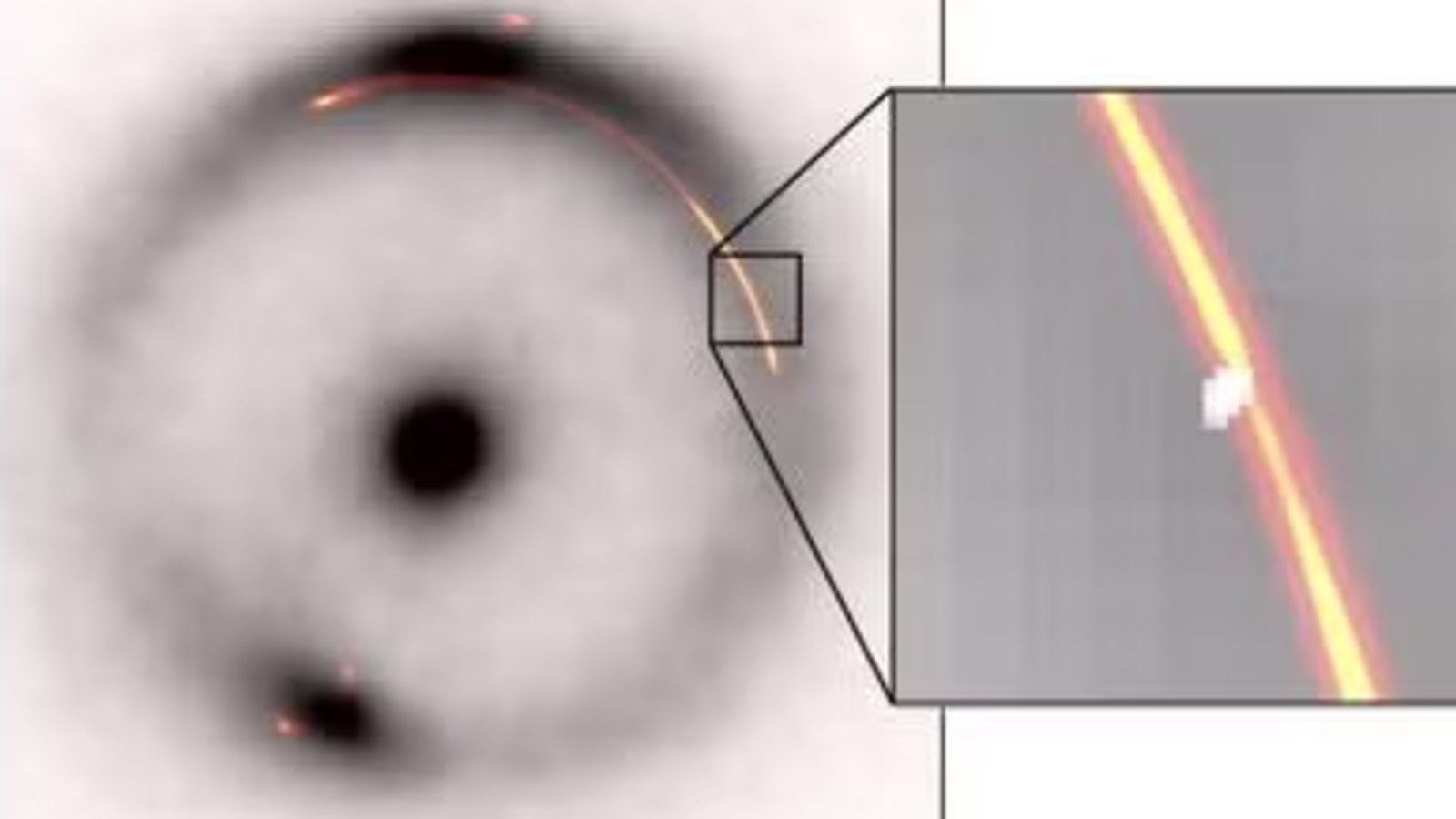
This object is about 1 million times heavier than the Sun, which seems like a lot of weight. However, this would actually be about 100 times smaller than the previous record holder for the smallest mass object ever detected by gravitational lensing.
The research team discovered the object by combining data from radio astronomy observatories around the world, including the Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia, the Very Long Baseline Array in New Mexico, and the European Very Long Baseline Interferometer Network. This allowed the researchers to achieve observational power comparable to an Earth-sized telescope, helping them detect such subtle fluctuations in the data. But there was so much information that researchers had to come up with new ways to categorize it.
“The data are so large and complex that we had to develop new numerical approaches to model them,” Simona Begetti, an astronomer at Germany’s Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics and co-author of both new studies, said in a statement. “This was not easy because it had never been done before.”
Although they can’t say for sure, researchers are confident that this new object is a small blob of dark matter. Dark matter is an invisible substance that makes up 27% of the known universe and does not interact with light. This is not surprising, given that gravitational lensing is one of the only ways dark matter can be detected and measured, and that Einstein rings and other distorted objects are one of the greatest weapons to uncover its true identity.
Finding isolated clumps of dark matter like this is particularly useful for testing the cold dark matter theory. The theory assumes that dark matter can only aggregate if it moves at relatively slow speeds, meaning it releases relatively little energy.
And researchers predict that these clumps are much more common than we currently realize. “We predict that all galaxies, including our Milky Way, are filled with clumps of dark matter, but it will take a huge number of calculations to discover them and convince the community of their existence,” Veghetti said.
To date, only three other similarly small potential dark matter clumps have been identified, the researchers wrote. But new methodologies are making it easier to find more clumps around existing Einstein rings, and the number of known rings is also rapidly increasing, thanks to the James Webb Space Telescope, which has proven to be very good at finding them.
“Now that we have discovered one, the question now is whether we can discover more,” Devon Powell, an astronomer at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics and co-author of both new studies, said in a statement.
Source link