GGP provides high-quality open-source data to monitor and understand family formation dynamics and other life course trajectories within societies at the individual level.
Populations change due to changes in three social areas: birth rates, mortality rates, and migration. This means new children are born, people die, and people move across countries. Monitoring such demographic trends is necessary to observe, understand, and predict population changes. Governments, businesses, and nonprofit organizations can use insights into how populations change and adapt to new conditions to inform policy, understand future demands, and potentially support vulnerable groups. Therefore, the availability of reliable and representative information, or data, is paramount to studying population dynamics. To ensure data quality and comparability across countries, international data collection efforts are best organized in research infrastructures (RIs). Within the European Union (EU), RIs operating on a non-economic basis can apply for registration on the European Strategic Forum for Research Infrastructures (ESFRI) Roadmap. This can be understood as a stamp of approval for the scientific and social relevance of RI.
Main research infrastructure in population dynamics
The Generations and Gender Program (GGP) is the only European-led comparative research infrastructure focused on demographic and social dynamics within families.
GGP was founded in 2000 and is managed by a consortium of international knowledge institutions. GGP’s headquarters are located at the Netherlands Institute for Interdisciplinary Demography (NIDI) in The Hague, Netherlands. In 2021, GGP was incorporated into the European Roadmap for Research Infrastructures (ESFRI). GGP is scheduled to become the European Research Infrastructure Consortium (ERIC) in 2027. The program’s primary tool for data collection is the Generation and Gender Survey (GGS). GGS collects new information about the lives of (young) adults, i.e. people aged 18 to 79, within a country or region. The GGS tracks the experiences and changes that individuals undergo in their personal lives through a longitudinal design that includes both past and prospective information. These representative data are rich in indicators that describe the national situation. GGS currently consists of two rounds of data collection.
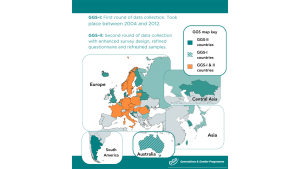
The first round (GGS-I) began in 2004 as a three-wave panel study with a three-year time interval. This first round collected information from more than 200,000 individuals in 19 countries. The second round (GGS-II) started in 2020. Data collection is currently in progress. GGS Round 2 is characterized by a revised questionnaire, an enhanced survey design, and an updated sample. The infographic above provides an overview of all countries and territories that have conducted at least one GGS. Many European countries participate in both data collection rounds, making the GGS an excellent data source for comparative country studies in the European context. In recent years, GGP has spread its wings to other continents, with data collection efforts also taking place in South America (Uruguay and Buenos Aires) and Asia (South Korea, Taiwan, and Hong Kong).
Comparing people’s life course events and trajectories
Influential factors such as upbringing, education, partner choice, general health, and personal beliefs contribute to shaping people’s life courses. Although some people’s life courses exhibit a high degree of stability, most people’s lives are characterized by successive stages characterized by major events and role changes. Important topics that can be studied using GGP data are partner selection, family formation, role division within households, intergenerational relationships, and the socio-economic situation of young people, families, and other household types. Additionally, the GGP provides information for the purposes of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Indicators of gender autonomy and contraceptive use are measured repeatedly within the program. The GGP database contains authoritative information on over 300,000 individuals. GGP has over 6,000 users worldwide who work together to create a rich source of up-to-date knowledge. Considering this scope, GGP, together with GUIDE, SHARE, and ESS, occupies an important position in the group of survey data research infrastructures that capture people’s entire life course.
Evidence-based policy making and informed social debate
GGPs have a lasting impact on policy areas. GGP data has informed strategic plans, policy reports, and parliamentary debates in many countries, including Austria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Estonia, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Lithuania, Moldova, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. International organizations such as UNFPA, OECD, WHO, and European Commission cite GGP products in their analyses.
A recent scan identified over 500 policy documents that reference GGP or GGS, confirming infrastructure’s extensive policy footprint and institutional recognition. To keep users and stakeholders informed, GGP regularly hosts webinars and policy briefings. To stay up to date on developments within the program and the release of new data, sign up for GGP’s free monthly newsletter, follow our LinkedIn page, or visit our website.
This article will also be published in the quarterly magazine issue 24.
Source link

