The NATWORK project is working to build and deploy the first economically realistic, energy-efficient, and viable 6G cybersecurity and resiliency framework.
Adopting a holistic approach and considering all elements of the cross-sector business environment to address the diverse requirements and challenges that arise, NATWORK aims to establish and deploy an economically realistic, energy-efficient, and viable bio-inspired artificial intelligence (AI)-based 6G cybersecurity and resilience framework for intelligent networking and services.
Nutwork’s vision
This project aims to develop a new AI-powered self-adaptive security mechanism for 6G networks based on resilient biomimetic principles. Our vision spans six key pillars.
Detailed extension definition of 6G architecture
By providing E2E security. Facilitate secure-by-design configuration and migration of secure distributed computing networks in the edge-to-cloud continuum with new 6G cloud-native slices. Deliver reliable and accountable control powered by net-zero AI to enable flexible and attack-resistant networks. Physical layer security that supports persistent self-healing of encryption-free wireless links. Deployment and experimental implementation of security modules in relevant use cases. Assessing, validating, and validating the performance of security frameworks.
learn from nature
The NATWORK consortium details biobased network key performance indicator (KPI) management and security concepts. The analogy between 6G networks and a complex biological structure (the human body) is employed in the NATWORK design, where the immune system learns from past security incidents, anticipates potential future threats, and adjusts security protocols to respond to changing conditions.
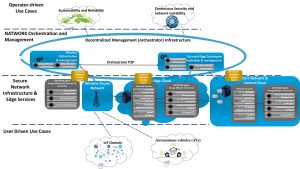
According to this paradigm, 6G network resource management tools optimize Service Layer Agreement (SLA) KPIs and sustainability, as well as glucose distribution metabolism. Security for 6G services is achieved in a sustainable manner, including homeostasis to prevent tissue degradation under threat, selective glucose distribution, and iron sequestration against pathogens. The concept incorporates AI to detect anomalies in new and unknown threats, such as the self-learning ability of B and T cells.
Network work results
NATWORK use case scenarios, requirements, and technical specifications were developed with the first version of the architecture. NATWORK’s architecture mimics the step-by-step behavior of biological immunity. Its first layer of defense employs AI-based proactive mechanisms that dynamically change the available attack surface to thwart intruders. The second layer uses adaptive AI/ML models to classify detected threats and initiate mitigation actions, while learning from past security incidents and being trained to predict and mitigate future threats. This knowledge ensures increased situational awareness and adaptability. Therefore, NATWORK develops an AI-driven cybersecurity autoimmune system.
Significant progress has been made towards the development of the first release of NATWORK technology. The consortium achieved preliminary results, conducted tests on an experimental testbed, and defined the framework required for final integration. These refer to the expected outcomes of the technical work, namely the expected technology components, including secure-by-design orchestration and management, per-runtime payload security, intelligent networking, CTI and explainability, physical layer threat modeling, AI-powered anti-jamming, and RIS defense mechanisms.
Preparatory activities are underway for the start of the first round of the NATWORK pilot. These include defining an evaluation framework and drafting a pilot specification. A roadmap for commercial use of the results was explored and plans for partner use were developed. The results of the first 18 months of project activity were disseminated through targeted events and 35 scientific publications.
NATWORK also seeks to influence 6G standards and policy. This project complies with EU regulations such as GDPR and Cybersecurity Law. Additionally, the project will contribute to the EU’s low carbon goals by enabling a secure, sustainable and high-performance 6G ecosystem, strengthening Europe’s global 6G leadership.
technology development
NATWORK continues to develop and improve a series of new technological achievements. These include:
Dynamic Moving Target Defense (MTD) framework for end-to-end security. AI-native 6G architecture that utilizes a cross-layer distributed approach based on secure federated learning. Secure-by-design 6G cloud-native slice configurator. Security as a Service (SECaaS) that is platform independent, always sustainable, covers all threats, supports all payload formats, and is intent-based and adjustable. Advanced distributed orchestration and management services powered by AI. Detailed software runtime monitoring to detect DoS attacks. AI-powered anti-jamming and RIS protection module. Decentralized node (self-)authentication and trust regulation. In-network security and data plane security framework.
use case
The consortium identified four use cases (UCs) that enable the demonstration of a security framework and thorough evaluation, validation, and validation of its performance, which were further divided into 16 sub-use cases. An example of using NATWORK is:
UC1: 6G slice and service sustainability and reliability
UC1’s aim is to explore innovative energy solutions that can support reliable connectivity and high-quality services, while reducing energy costs and minimizing environmental impact.
UC2: Anti-jamming technology for self-driving cars
UC2 refers to the use of machine learning and AI techniques to detect, classify, and mitigate jamming attacks in real-time by analyzing signal patterns.
UC3: IoT Security
UC3 focuses on the security and privacy of IoT devices and their data in 6G networks by leveraging advanced threat detection and mitigation mechanisms.
UC4: Increase network variability with continuous security
UC4 aims to ensure robust and continuous security in highly dynamic and heterogeneous 6G network architectures by employing machine learning and AI to provide real-time security analysis, adaptation, and proactive defense against emerging threats across a variety of devices, services, and mobile users.
About the project

NATWORK is being implemented by a consortium of 15 participants from eight EU countries and two associated countries (Switzerland and the United Kingdom). This project is coordinated by the Hellas Information Technology Institute Research and Technology Center (CERTH-ITI). The total budget is over 6.1 million euros.
Disclaimer

This project is co-funded by the Smart Networks & Services Joint Undertaking (SNS JU) under the European Union’s Horizon European Research and Innovation Program for European participants, the Swiss Cantonal Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) for participants in Switzerland, and UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) for participants in the United Kingdom under grant agreement number 101139285.
This article will also be published in the quarterly magazine issue 24.
Source link

