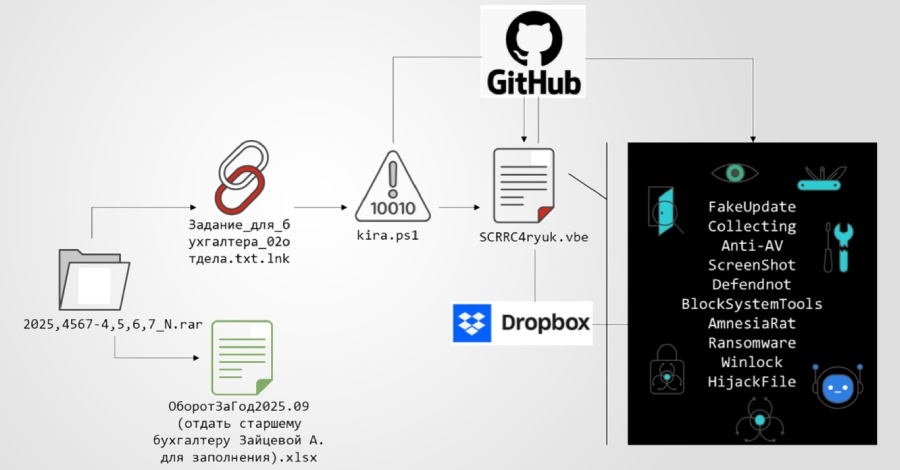
A new multi-stage phishing campaign was observed targeting users in Russia using ransomware and a remote access Trojan called Amnesia RAT.
“This attack begins with a social engineering lure delivered via business-themed documents designed to appear routine and harmless,” Fortinet FortiGuard Labs researcher Cara Lin said in technical details released this week. “These documents and accompanying scripts act as visual distractions, directing victims to fake tasks and status messages while the malicious activity runs silently in the background.”
This campaign stands out for several reasons. First, use multiple public cloud services to distribute different types of payloads. GitHub is primarily used to distribute scripts, while binary payloads are staged to Dropbox. This separation complicates takedown efforts and effectively increases recovery.
Another “defining feature” of the campaign, according to Fortinet, is the operational exploitation of Defensenot to disable Microsoft Defender. Defendnot was released last year by a security researcher who goes by the online alias es3n1n as a way to trick security programs into believing another antivirus product was already installed on a Windows host.
The campaign uses social engineering to distribute multiple decoy documents and compressed archives containing malicious Windows shortcuts (LNKs) with Russian filenames. LNK files use a double extension (“Задание_для_бухгалтера_02отдела.txt.lnk”) to give the impression that they are text files.
When run, it executes a PowerShell command and retrieves the next stage PowerShell script hosted in a GitHub repository (‘github’).[.]com/Mafin111/MafinREP111″) acts as a first-stage loader to establish a foothold, prepare the system to hide evidence of malicious activity, and hand over control flow to subsequent stages.
“The script first suppresses visible execution by programmatically hiding the PowerShell console window,” Fortinet said. “This removes all direct visual indicators that the script is being executed. It then generates a decoy text document in the user’s local application data directory. Once written to disk, the decoy document is automatically opened.”
Once the document is shown to the victim to continue the ruse, the script uses the Telegram Bot API to send a message to the attacker, informing the operator that the first stage was successfully executed. After an intentionally introduced delay of 444 seconds, the PowerShell script runs a Visual Basic script (‘SCRRC4ryuk.vbe’) hosted in the same repository location.
This has two important benefits: it keeps the loader lightweight and allows the attacker to update or replace the payload’s functionality on the fly without making changes to the attack chain itself.

The Visual Basic script is highly obfuscated and acts as a controller that assembles the next stage payload directly in memory, avoiding artifacts left on disk. The final stage script checks to see if it is running with elevated privileges and, if not, repeatedly displays User Account Control (UAC) prompts to force the victim to grant the necessary permissions. The script pauses for 3,000 milliseconds between attempts.
In the next phase, the malware initiates a series of actions to suppress visibility, disable endpoint protection mechanisms, conduct reconnaissance, prevent recovery, and finally deploy the main payload.
Configure Microsoft Defender exclusions so that the program does not scan the ProgramData, Program Files, Desktop, Downloads, and system temporary directories Turn off additional Defender protection components using PowerShell Deploy fake antivirus products to avoid registering with the Windows Security Center interface and disable Microsoft Defender itself to avoid potential conflicts Screenshots using a dedicated .NET module downloaded from a GitHub repository Performs reconnaissance and monitoring of the environment via capture Captures the screen every 30 seconds, saves it as a PNG image, and extracts the data using the Telegram bot Tampers with registry-based policy controls to disable Windows administrative and diagnostic tools Implements a file association hijacking mechanism, upon opening a file with a specific predefined extension, a message is displayed to the victim instructing them to contact the attacker via Telegram
One of the final payloads deployed after successfully defeating security controls and recovery mechanisms is the Amnesia RAT (‘svchost.scr’). It is obtained from Dropbox and allows extensive data theft and remote control. It is designed to steal information stored in web browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, Discord, Steam, and Telegram, as well as system metadata, screenshots, webcam images, microphone audio, clipboard, and active window titles.

“RATs enable full remote interaction, including enumerating and terminating processes, executing shell commands, deploying arbitrary payloads, and executing additional malware,” Fortinet said. “Extraction is primarily performed over HTTPS using the Telegram Bot API. Large datasets may be uploaded to third-party file hosting services such as GoFile, and the download link is relayed to the attacker via Telegram.”
Overall, Amnesia RAT facilitates credential theft, session hijacking, financial fraud, and real-time data collection, turning it into a comprehensive tool for account takeover and follow-on attacks.
The second payload delivered by the script is ransomware derived from the Hakuna Matata ransomware family and is configured to encrypt documents, archives, images, media, source code, and application assets on the infected endpoint, but not before terminating any processes that may interfere with its functionality.
Additionally, the ransomware monitors clipboard contents and silently changes cryptocurrency wallet addresses and reroutes transactions in attacker-controlled wallets. The infection sequence ends with a script that deploys WinLocker to restrict user interaction.
“This attack chain shows that modern malware campaigns can compromise entire systems without exploiting software vulnerabilities,” Lin concluded. “By systematically exploiting native Windows features, management tools, and policy enforcement mechanisms, attackers disable endpoint defenses before deploying persistent monitoring tools or destructive payloads.”
To combat Defensenot’s abuse of the Windows Security Center API, Microsoft recommends that users enable tamper protection to prevent unauthorized changes to Defender settings and monitor suspicious API calls and changes to the Defender service.

This development comes after the human resources, payroll, and internal administration departments of a Russian corporation were targeted by threat actor UNG0902 to deliver an unknown implant called DUPERUNNER, which is responsible for loading the command and control (C2) framework AdaptixC2. This spear phishing campaign, codenamed Operation DupeHike, has been ongoing since November 2025.
According to Seqrite Labs, the attack uses a decoy document centered around themes related to employee bonuses and internal financial policies to persuade the recipient to open a malicious LNK file in a ZIP archive, leading to the execution of DUPERUNNER.
The implant connects to an external server to retrieve and display the decoy PDF document. Meanwhile, system profiling and AdaptixC2 beacon downloads run in the background.
In recent months, Russian organizations may also have been targeted by another threat actor tracked as Paper Werewolf (also known as GOFFEE). GOFFEE distributed a backdoor called EchoGather using artificial intelligence (AI)-generated decoys and DLL files compiled as Excel XLL add-ins.
“Once activated, the backdoor collects system information and communicates with a hard-coded command-and-control (C2) server to support command execution and file transfer operations,” said Intezer security researcher Nicole Fishbein. “Communicate with the C2 over HTTP(S) using the WinHTTP API.”
Source link