PFOA contamination has become one of the world’s most pressing and intractable water safety challenges, with the toxic “forever chemical” now being detected in drinking water supplies, groundwater, and ecosystems far from its source.
Now, researchers at Shenyang Agricultural University have unveiled a promising new weapon in the fight against PFOA pollution, harnessing an unexpected ally from the ocean: marine algae.
A newly developed material made from algae-derived biochar and enhanced with nanotechnology has demonstrated superior ability to capture and degrade one of the most stubborn toxic chemicals present in water worldwide.
Persistent pollutants spread around the world
Perfluorooctanoic acid, also known as PFOA, belongs to the broader PFAS family of permanent chemicals.
These compounds received their nickname due to their extreme chemical stability caused by strong carbon and fluorine bonds that withstand heat, sunlight, and most conventional processing methods.
As a result, PFOA contamination extends far beyond industrial sites, appearing in drinking water, groundwater, sediments, and even remote ecosystems.
The health implications are serious. Exposure to PFOA has been linked to cancer, immune system disruption, and developmental problems, leading regulatory authorities around the world to impose increasingly stringent limits on permissible concentrations in drinking water.
However, effective and low-cost removal of PFOA remains a major technical challenge.
Turning seaweed into high-tech solutions
New research describes an innovative approach to blending sustainable materials with advanced photocatalysts.
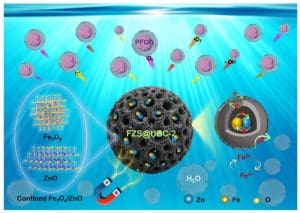
Scientists used Ulva, a fast-growing and widely available marine algae, to produce a porous biochar framework. This biochar acts as a scaffold for iron oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles, forming a microscopic cage-like structure.
This structure allows the material to function as a “nanoreactor.” It actively degrades contaminants rather than simply trapping them, providing a dual-action solution to PFOA contamination that combines adsorption and chemical degradation.
How light affects the purification process
Photocatalysts are at the heart of the new material’s performance. When exposed to light, metal oxide nanoparticles generate highly reactive oxygen species that can attack complex organic molecules such as PFOA.
In traditional systems, these reactive species are only present for short periods of time and have very short distances to travel, which limits their effectiveness.
The confined structure of algae-based biochar changes its dynamics. By creating a tightly controlled reaction space, the nanoreactor increases the chances of reactive species colliding with PFOA molecules before dissipating.
This significantly improves degradation efficiency and helps overcome one of the biggest barriers in treating PFAS-contaminated water.
Impressive test results
In controlled experiments, the optimized catalyst removed more than 97% of PFOA contamination from water within just 4 hours. Equally important, the material has proven to be durable and capable of maintaining high performance over multiple reuse cycles.
Built-in magnetic properties add further practical benefits. After treatment, the catalyst can be quickly recovered from the water using an external magnetic field, reducing waste and simplifying recovery in practical applications.
Designed for real water conditions
In addition to high removal rates, the new materials showed strong adaptability. It remained effective over a wide pH range and in the presence of common dissolved ions that often interfere with water treatment processes.
This resilience suggests that it may perform well not only in laboratory environments but also in complex natural and industrial water systems affected by PFOA contamination.
The porous biochar structure plays an important role here. The large surface area maintains a uniform dispersion of nanoparticles, prevents agglomeration, and reduces the distance between pollutants and reactive species, promoting degradation reactions.
A step towards sustainable water purification
This study demonstrates the increasing potential of biochar-based materials in environmental engineering.
This study presents a more sustainable and cost-effective strategy to combat emerging pollutants by converting renewable marine biomass into high-performance photocatalysts.
Although further testing and expansion is required, this study provides new insights into how smart material design can address the persistent challenge of PFOA contamination.
Source link

