Immediately after the Big Bang, the newborn universe was a wild and hot place. In that cosmic soup, primordial black holes, the universe’s first black holes formed from pockets of extremely dense matter, could soon take shape.
For many years, our understanding of these objects, especially small objects, was that they would eventually simply disappear through a quantum process called Hawking radiation. It seemed like fate.
But new research published in January on the preprint database arXiv opens up a different path. The study argues that these objects were not always shrinking, but in some cases may have grown, absorbing radiation from the early universe and becoming cosmic devourers.
you may like
This unexpected appetite doesn’t just change the individual fates of the nascent black holes. It also changes the way we view the cosmic past. And crucially, it changes the search for dark matter, the invisible scaffolding that holds galaxies together.
hungry newborn baby
Primordial black holes are an interesting idea in cosmology. Unlike regular black holes, which are born from the collapse of stars, these objects are thought to have formed from the extreme density of the universe’s nascent soup in the first moments after the Big Bang. They can range from microscopic sizes to masses larger than the Sun.
For a long time, general relativity has told us that these objects, especially small objects, will slowly lose mass due to Hawking radiation. They just evaporate and disappear.
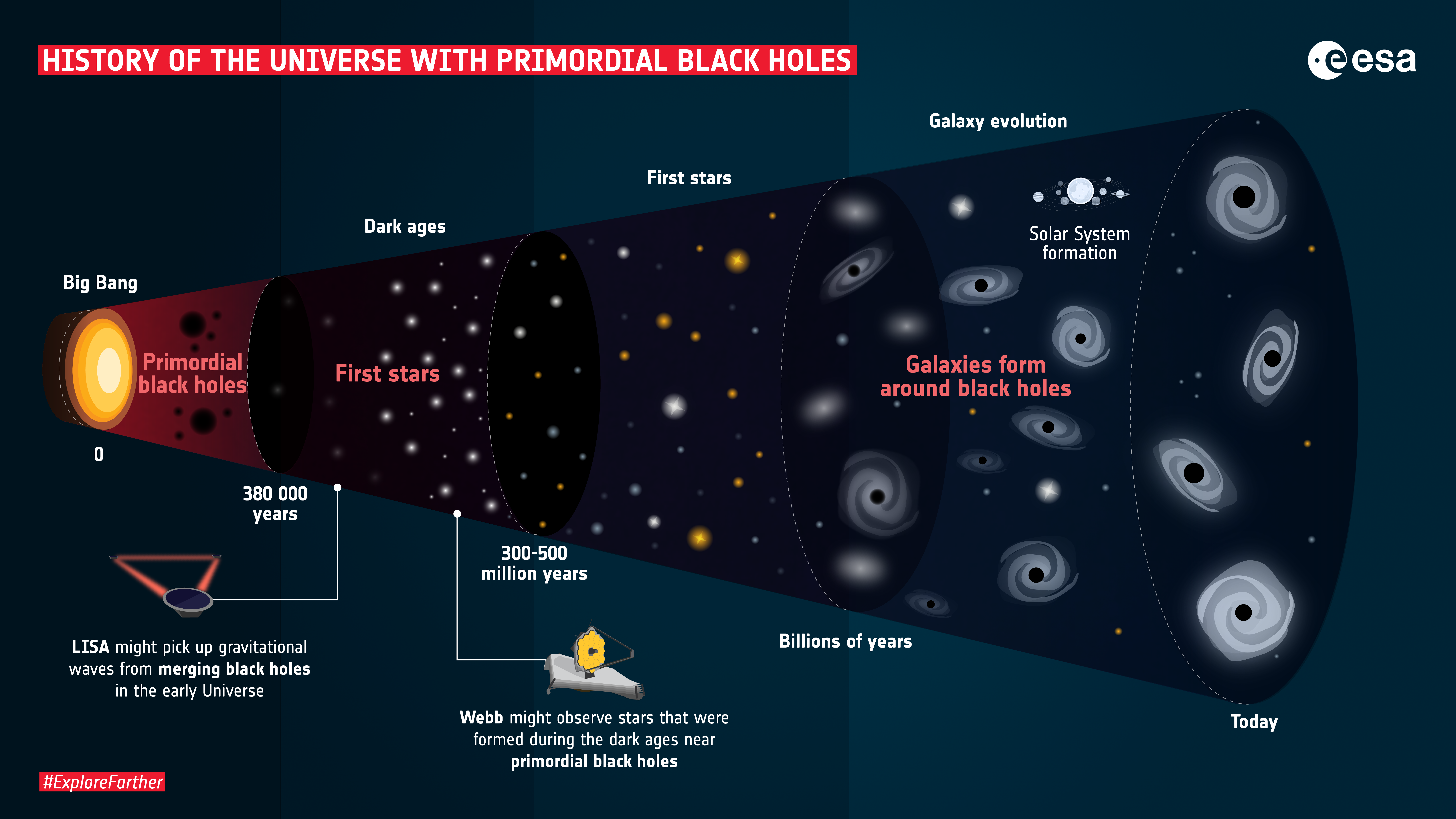
The story changes dramatically here. The early universe was not just a quiet vacuum around these primordial black holes. It was a thick, hot soup, full of radiation, with photons flying everywhere.
This new study adds an important piece to the puzzle of direct absorption of thermal radiation. If the decay efficiency of a primordial black hole exceeds a certain value calculated in the new study, it will not just evaporate slowly; It begins to feed. These black holes will go silent and become hungry devourers of the universe, a new study suggests.
This new understanding changes everything about how we picture the early universe and the fate of these ancient objects. Their ability to grow means they can live much longer than we previously thought, leading to extended lifespans and considerable mass gains.
If primordial black holes can grow by absorbing radiation, a much wider range of initial masses could still exist today and serve as the universe’s invisible dark matter. Research has shown that this range expansion is highly dependent on something called the absorption efficiency parameter, a measure of how quickly and efficiently a black hole can feed on surrounding matter.
For example, if this parameter is 0.3, the tolerance for primordial black holes to form and become dark matter increases from 10^16 grams to 10^21 grams. If the parameter is 0.39, the range is 5*10^14 grams to 5*10^19 grams. Previously, it was thought that primordial black holes could not be this massive and were still responsible for dark matter.
This work makes us rethink many things about the first moments of the universe. It forces a fundamental reassessment of how these objects evolve and their potential to explain the mystery of dark matter. This is not just a small adjustment to the model. It’s a new chapter in our cosmic story. We thought we knew the life cycles of these objects, but it turns out the universe has other plans.
Black Hole Quiz: How vast is your knowledge about the universe?
Source link

