Astronomical communities are ravaging newly discovered “interstellar objects.”
The race is currently underway to study an alien intruder named 3i/Atlas before leaving forever.
“We only have one shot on this object, but it disappeared forever,” Daryl Seligman, an astronomer at Michigan State University and lead author of a new paper on objects, told Live Science. “So we want a lot of information from every observatory as much as possible.”
You might like it
Related: Watching the newly discovered “interstellar visitor” 3i/Atlas film towards us in its first live stream
Experts say studying 3i/Atlas could potentially teach you how alien star systems and deplanets form.
The first discovery
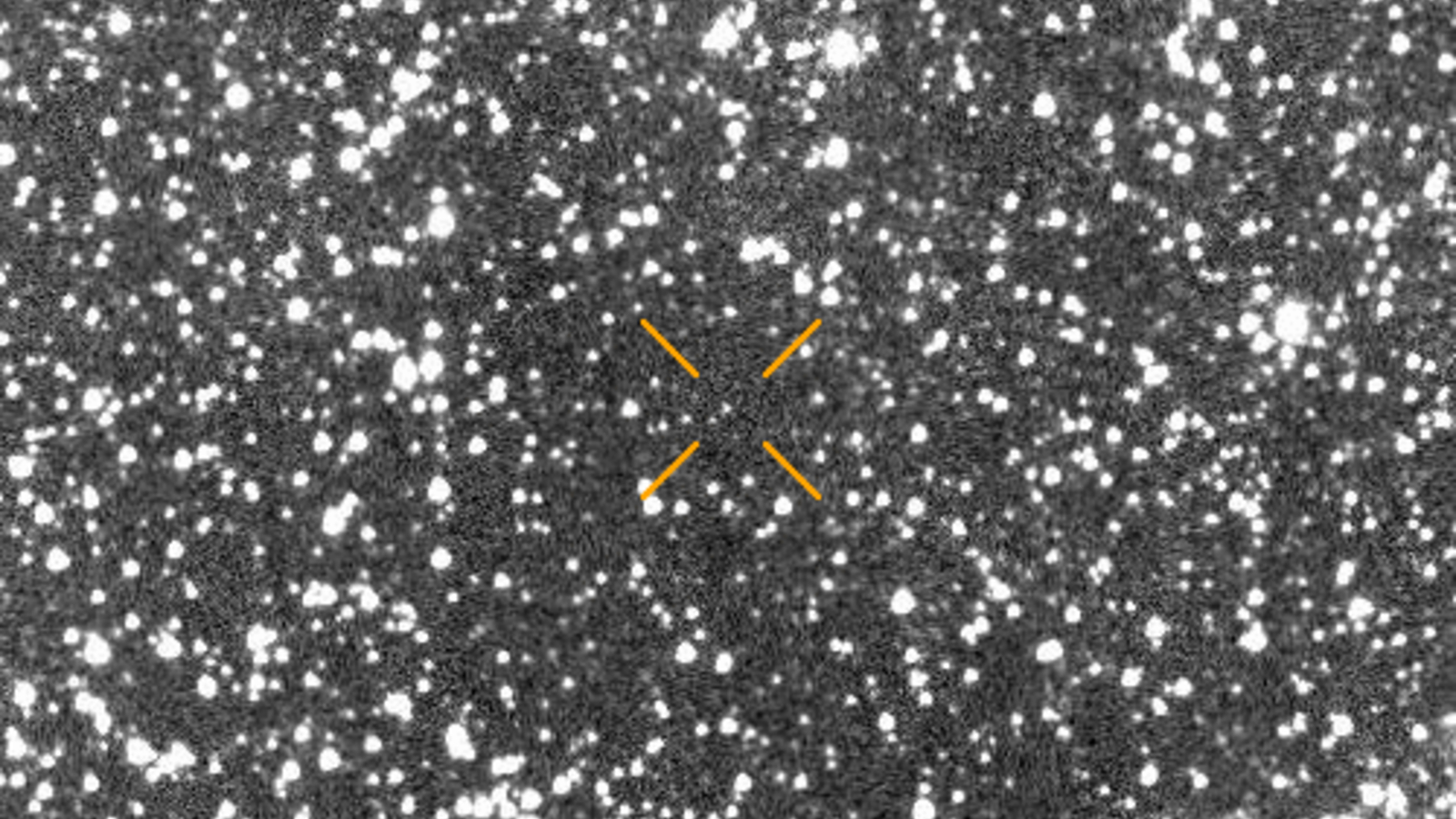
3i/Atlas was discovered in data collected by the Last Alert System of Asteroid Terrestrial Impact (ATLA) on July 1, and quickly stimulated the interests of researchers with orbits exceeding 130,000 mph (210,000 km/h). Within 24 hours of discovery, NASA confirmed it was an interstellar object.
A day later (July 3), a group of over 40 astronomers led by Seligman uploaded their first paper to the Prelint database Arxiv, describing polar entities. All data so far shows that 3i/Atlas is a large comet surrounded by clouds of ice, dust and gas.
Prior to this discovery, only two other interstellar objects (ISOs) had been discovered. 1i/’Oumuamua, a space rock discovered in 2017. 2i/Borisov, a comet discovered in 2019. This makes the newly discovered comet particularly appealing to astronomers.
However, there is a limited window to investigate 3i/Atlas. Currently, comets about 4.5 times more than Earth than Earth will reach the closest point to the Sun before leaving the solar system on October 30th. Also, from late September to early December, it will become invisible while being placed on Earth on the other side of the sun.
Observing interstellar visitors

Over the next few weeks and months, researchers will try to use “all telescopes” to make observations of 3i/Atlas, a planetary scientist at the University of Bordeaux in France.
This is especially true for observatory observatory in the Southern Hemisphere. This gives a better view of Aster Taylor, a graduate student at the University of Michigan, an increasingly bright comet and co-author of the ARXIV study.
Experts are particularly excited by the 3i/Atlas’ imaging potential using the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, the world’s most powerful optical telescope, which recently released its first image. Located in Chile, the observatory has already proven to be proficient in asteroid imaging, and will undoubtedly target interstellar comets once it has come fully online in a few months.
Meanwhile, James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Hubble Space Telescope helped to clarify the chemical composition of intruders due to the ability to study objects of electromagnetic spots Pedro Bernardinelli, a planetary scientist at the University of Washington Dirac Institute.
Some researchers have proposed using NASA’s Mars rover to take photos of comets. Robots have previously been used to spy on dangerous solar spots hiding beyond the sun.
Another interesting option is to send the spacecraft and collect samples from 3i/Atlas. However, the general consensus among experts is that such a mission is unlikely to occur.
Alien Star System

Studying 3i/Atlas offers an unusual opportunity to gather insights into alien star systems and potential deplanets.
“Interstellar objects are probably leftovers from the formation of exoplanets,” Raymond said. “Studying them will allow us to open windows to understand the formation and evolution of other planetary systems.”
In this way, “connecting the solar system with the galactic environment” like ISOS, 3i/Atlas, is a doctoral candidate at Princeton University who previously studied ISOS, told Live Science.
It is still unknown where 3i/Atlas came from, but it could be possible to identify its origin, especially if researchers can determine how old it is, Canadian astronomer Wes Fraser of the National Research Council, told Live Science in an email. And once the comet reaches perihelion, the amount of ice and other “volatile” material burned by the intruders can help narrow this down, Fraser added.
But even so, “it’s probably not possible to pin it into a single star system,” Taylor insisted.
Source link

