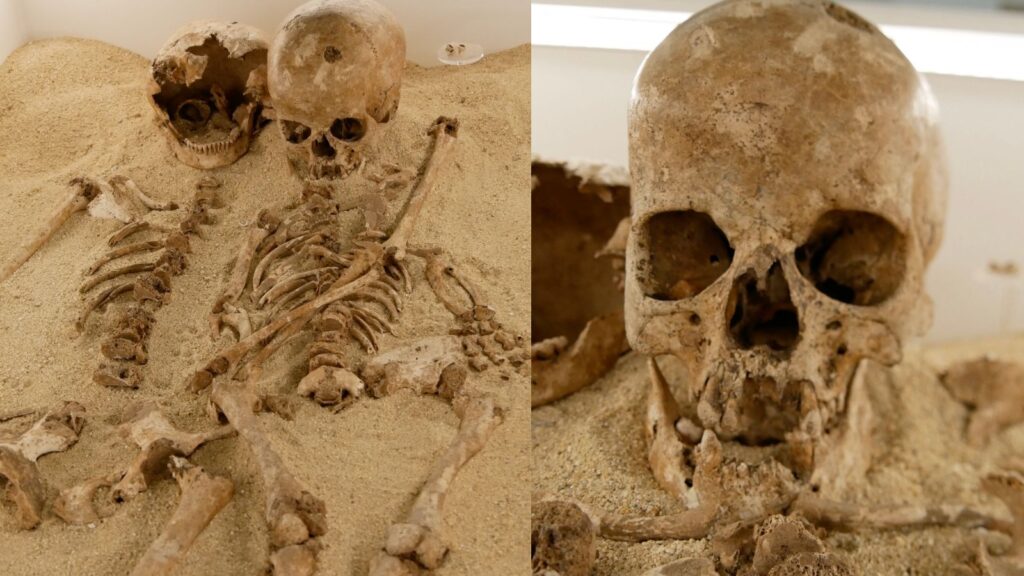
A Stone Age man buried in an Italian cave 12,000 years ago suffered from a rare genetic disorder that caused his limbs to become short, a new study has found.
DNA analysis of her skeleton revealed that she was a teenage girl with a rare form of dwarfism. Researchers say this discovery is the earliest DNA diagnosis of a genetic disease in an anatomically modern human.
“This is a real breakthrough for medicine, as it is the earliest DNA-confirmed genetic diagnosis ever performed in humans, the earliest diagnosis of a rare disease, and the earliest familial genetic case,” study co-author Adrian Daly, a researcher in endocrinology at Liege University Hospital in Belgium, told Live Science via email. “Identifying with near certainty a single base change in a gene in a person who died between 12,000 and 13,000 years ago is the first such diagnosis in about 10,000 years.”
you may like
Researchers discovered that the teenager, dubbed “Romito 2” after the cave where the remains of her and eight other prehistoric hunter-gatherers were discovered in 1963, had a rare genetic disorder called acrochromosomal dysplasia, Maroteau type (AMDM). In this condition, the limbs become extremely short, especially the forearms, front legs, hands, and feet.
AMDM is caused by mutations on both chromosomes in the NPR2 gene, which plays an important role in bone growth. As a result of her condition, Romito 2 “would have faced challenges in traveling over distance and terrain, and limitations in elbow and hand movement would have affected her daily activities,” Daly and colleagues wrote in the study, published Wednesday (January 28) in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Romito 2 was approximately 3 feet 7 inches (110 centimeters) tall. Contrary to previous studies that claimed the skeleton was male, DNA testing using material taken from the left inner ear revealed that Romito 2 was female. She was buried in an embrace with an adult nicknamed “Romito 1,” who was also buried in the limestone cave of Lomito in southern Italy.
DNA testing also revealed that Romito 1 is female and a first-degree relative of Romito 2, meaning they may be mother and daughter or sisters. Interestingly, Romito 1 was shorter than the average adult at the time, standing at 4 feet 9 inches (145 cm).
Analysis revealed that Romito 1 had one abnormal copy of the NPR2 gene, which may have somewhat restricted her growth. However, it was not as bad as Romito No. 2. Romito 2 had two abnormal copies of the gene, which caused him to exhibit more pronounced dwarfism.
Genetic material taken from the skeletons confirmed that Lomit 1 and Lomit 2 were from the Villabruna genetic population, a group of hunter-gatherers that expanded from southern Europe to central and western Europe about 14,000 years ago. Although researchers found no evidence of inbreeding, the population living near Lomit Cave was likely small, according to the study.
It is still unclear how Romito 1 and Romito 2 died as their bodies showed no signs of trauma. Lomit 2’s diet and nutritional status are similar to others buried in Lomit Cave, suggesting that a community cared for her.
“The challenges she faced were met by the provision of care by the family group,” the researchers said in the study.
Fernández, D. M., Llanos Liscano, A., Brück, F., Oberreiter, V., Ozdogan, K. T., Ceronet, O., Lucci, M., Beckers, A., Petrosyan, P., Coppa, A., Pignasi, R., and Daly, A. F. (2026). A case of NPR2-associated achromesome dysplasia 12,000 years ago. New England Medical Journal. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2513616
Source link