Cybersecurity researchers have revealed details of a patched vulnerability on the popular figma-developer-mcp Model Context Protocol (MCP) server. This vulnerability could allow an attacker to execute code.
Tracked as CVE-2025-53967 (CVSS score: 7.5), the vulnerability is a command injection bug caused by the unsanitized use of user input, opening the door to a scenario where an attacker can send arbitrary system commands.
According to GitHub’s advisory for the flaw, “The server constructs and executes shell commands using unverified user input directly within the command line string, which could result in shell metacharacter insertions (|, >, &&, etc.).” “If an exploit is successful, remote code can be executed with server process permissions.”
Given that the Framelink Figma MCP server exposes various tools for performing operations on Figma using artificial intelligence (AI)-powered coding agents such as Cursor, attackers can trick MCP clients with indirect prompt injection to cause them to perform unintended actions.

Cybersecurity company Imperva, which discovered and reported the issue in July 2025, described CVE-2025-53967 as a “design oversight” in the fallback mechanism, allowing malicious people to execute completely remote code, putting developers at risk of data leaks.
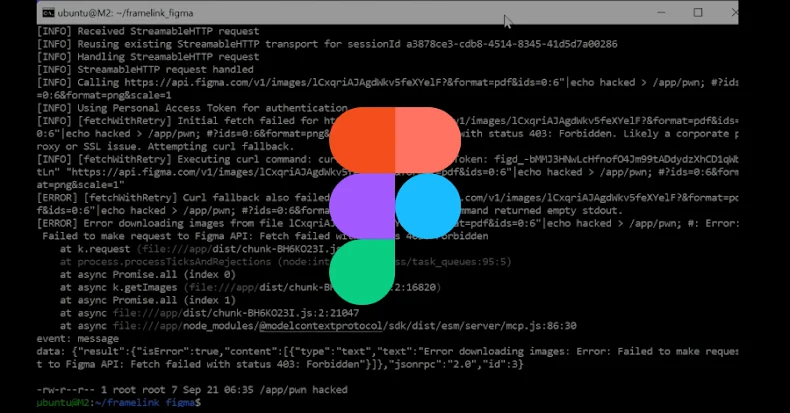
The command injection flaws “occur during construction of command line instructions used to send traffic to the Figma API endpoint,” said security researcher Yohann Sillam.
The exploitation sequence takes place over the next stage.
The MCP client sends an Initialize request to the MCP endpoint and receives the mcp-session-id that will be used for subsequent communication with the MCP server. The client uses the method tools/call to send JSONRPC requests to the MCP server and invokes tools such as get_figma_data and download_figma_images.
The heart of this issue lies in “src/utils/fetch-with-retry.ts” where you first try to retrieve content using the standard fetch API, and if that fails, you will proceed to running the curl command via child_process.exec. This will result in defective command injection.

“Because curl commands are constructed by inserting URLs and header values directly into shell command strings, malicious attackers could create specially designed URLs or header values that insert arbitrary shell commands,” Imperva said. “This can cause remote code execution (RCE) on the host machine.”
A proof-of-concept attack can cause a flaw by remote malicious attackers on the same network (such as public Wi-Fi or compromised corporate devices) sending a series of requests to a vulnerable MCP. Alternatively, an attacker could trick the victim into accessing a specially crafted site as part of a DNS rebind attack.
This vulnerability was resolved in figma-developer-mcp version 0.6.3, released on September 29, 2025. As a mitigation, we recommend that you avoid using child_process.exec on unreliable input and switch to child_process.execFile, which eliminates the risk of shell interpretation.
“As AI-driven development tools evolve and adoption progresses, it’s important to consider security as innovation is tailored,” the Thales-owned company said. “This vulnerability is a clear reminder that even tools intended to run locally can be a powerful intrusion point for attackers.”

The development comes after FireTail revealed that Google has chosen not to fix a new ASCII smuggling attack in Gemini AI chatbots that could be weaponized to create input that could slip through security filters and trigger unwanted responses. Other large-scale language models (LLMs) that are susceptible to this attack include DeepSeek and xAI Grok.
“And this flaw is particularly dangerous when LLMs like Gemini are deeply integrated into enterprise platforms like Google Workspace,” the company said. “This technology allows automated identity spoofing and organizational data poisoning, turning UI flaws into a potential security nightmare.”
Source link