Jupiter’s icy moon Europa appears to have life-friendly molecules on its surface.
Al Emran, a researcher at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, discovered ammonia on Europa’s surface while examining old data from the Galileo mission, which studied Jupiter and its moons from 1995 to 2003.
you may like
According to the statement, this is “the first such discovery on Europa” and therefore has important implications for the habitability of the icy moon, which is considered one of the most likely locations for extraterrestrial life in the solar system.
alien ice moon
Ammonia is a nitrogen-containing molecule that, along with carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and water, is one of the ingredients of life as we know it. Therefore, Emran said in the new paper, the discovery is of “astrobiological significance given the important role of nitrogen in the chemistry of life.”

Space and physics editor
“Europa is the fourth largest of Jupiter’s 95 known moons and is about 90% the size of Earth’s moon. Studies of Jupiter’s magnetic field suggest that Europa contains a deep layer of electrically conductive fluid, which scientists believe may be due to the moon’s ice. We think it’s likely a vast salty ocean trapped beneath the Earth’s crust. This hidden ocean makes Europa a prime candidate for extraterrestrial life in our solar system, but more detailed observations are needed to test this hypothesis. ”
The Galileo spacecraft operated in the Jupiter system from 1995 to 2003 until it ran out of fuel. Engineers deliberately steered the spacecraft toward the giant planet to avoid the risk of contaminating Europa and other icy moons. Although the mission ended operations more than 20 years ago, scientists sometimes find new insights in old datasets by using new tools and knowledge or by examining previously unscrutinized information.
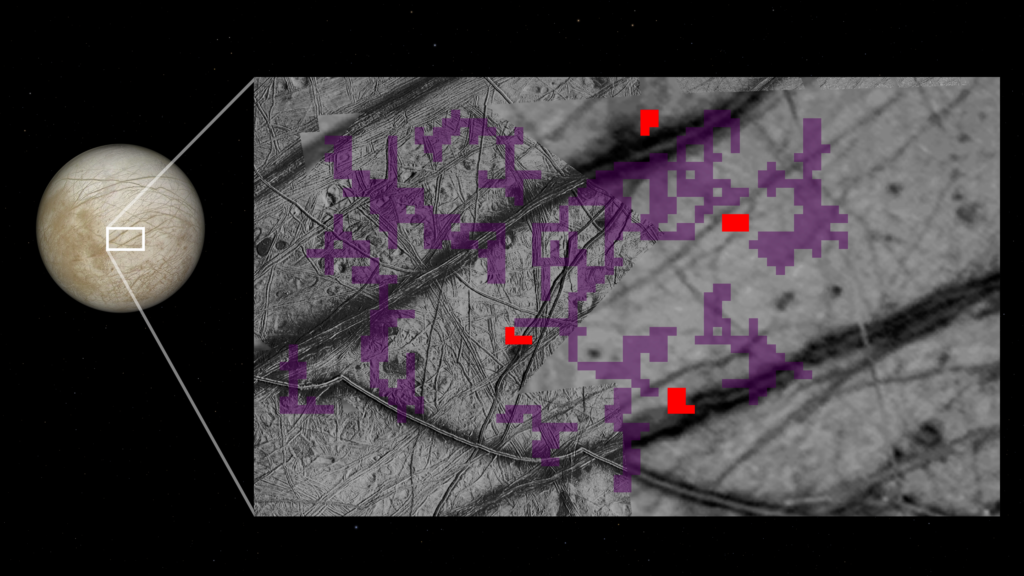
In a new study, NASA has discovered traces of ammonia near cracks in Europa’s icy surface. These cracks are believed to have contained liquid water containing ammonia compounds. Ammonia is like antifreeze, which lowers the freezing point of water, officials said.
NASA officials said in a statement that the ammonia could have come from “either the moon’s subsurface ocean or the shallow subsurface.” Ammonia does not remain in space for long because it is broken down by ultraviolet rays and cosmic radiation. The researchers explained that cryovolcanism, or cryovolcanism, likely pushed the ammonia compounds to the surface.
Follow-up missions may reveal further insights. Europa Clipper, launched in October 2024, is expected to arrive in the Jupiter system in April 2030. The mission will specifically look for chemical signs of habitability on the icy moon.
Source link