Cybersecurity researchers detail currently patched vulnerabilities in Google Cloud Platform (GCP), which could allow attackers to increase privileges with a cloud composer workflow orchestration service based on Apache Airflow.
“This vulnerability allows attackers with cloud composer edit permissions to escalate access to the default cloud build service account, which has high levels of access to the entire GCP service, such as the cloud build itself, cloud storage, and artifact registry.”
The drawback is called the confusing composer by Cybersecurity Company, and describes it as a variant of the confusing feature, a privilege escalation vulnerability affecting GCP’s cloud capabilities.
This disclosure comes weeks after Tenable details another privilege escalation vulnerability. GCP Cloud Run could potentially allow malicious actors to access container images and even insert malicious code, creating a cascade effect.
Like ImageRunner, ConfusedComposer is another example of the Jenga concept. This will result in the case of a cloud service provider building an existing service, which will be inherited from the service with a security issue to another service.

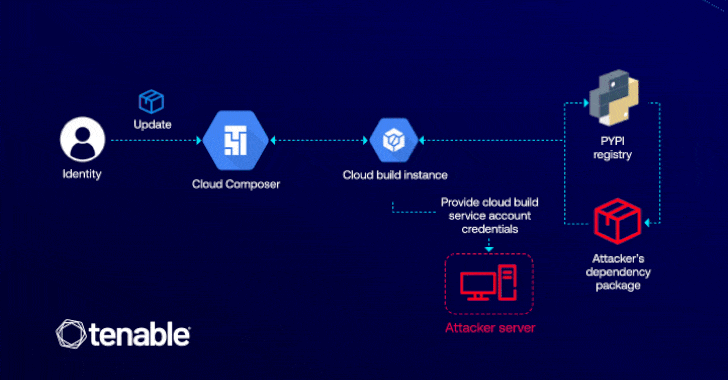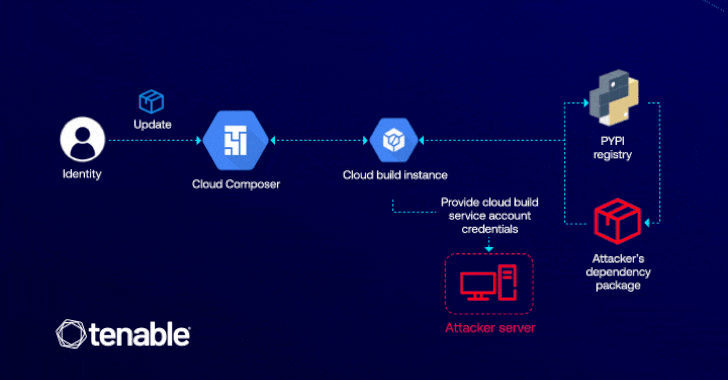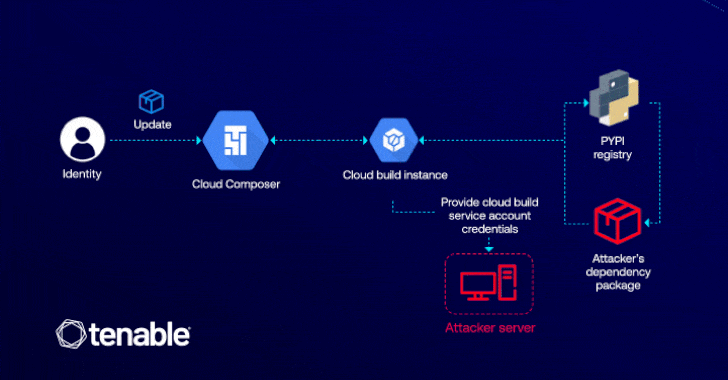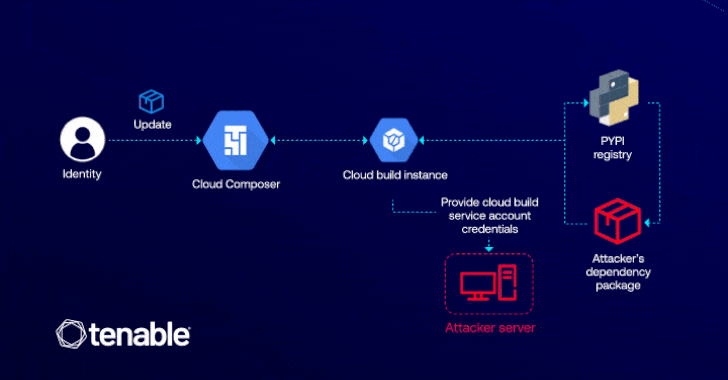
The exploit depends on attackers who have permission to edit a cloud composer environment (i.e. Composer.Environments.update) that could be leveraged to inject malicious Python package index (PYPI) packages that can escalate privileges through cloud builds.
The attack is possible because the cloud composer allows users to install custom beep packages in their environment, allowing adversaries to execute arbitrary code within the associated cloud build instance using installation scripts within the malicious package.
“Confusion is important as it reveals how behind-the-scenes interactions between cloud services are exploited through privilege escalation,” explained Matan. “In this case, the attacker only needs permission to update the cloud composer environment to access critical GCP services such as cloud storage and artifact registries.”
The successful exploitation of flaws allows attackers to suck up malicious code within the CI/CD pipeline, destroy and deploy services. Additionally, it could pave the way for backdoor deployments that can grant permanent access to compromised cloud environments.
Following responsible disclosure by Tenable, Google addressed the vulnerability as of April 13, 2025 by eliminating the use of a cloud build service account to install Pypi packages.

“The service accounts in your environment will be used instead,” Google said in its January 15, 2025 announcement.
“The Cloud Composer 2 environment created with Cloud Composer 2.10.2 already has this change. The Cloud Composer 3 environment already uses the service account for the environment and this change is not affected.”
This disclosure is because Varonis threat labs could reveal vulnerabilities in Microsoft Azure, allowing threat actors with privileged access to Azure SQL Server to modify configurations in a way that causes data loss to management actions. Microsoft has completely fixed the issue as of April 9, 2025, after being recognized on August 5, 2024.
According to the company, the destructive stored URL parameter injection vulnerability stems from the lack of character limits in server firewall rules created using Transact-SQL (T-SQL).
“By manipulating the name of a server-level firewall rule via T-SQL, threat actors with privileged access to Azure SQL Server can inject implants that remove any Azure resources that the user grants permission based on a specific user action.
“The impact of threat actors exploiting this vulnerability could be large-scale data loss for affected Azure accounts.”
Datadog Security Labs also shed light on a bug in Microsoft Entra ID Restricted Management Units to prevent attacker-selected users from being altered, deleted or disabled by global administrators.

“Privileged attackers used this bug to protect their accounts under their control and prevent containment by ENTRA ID administrators,” said security researcher Katie Knowles. This includes a variety of tasks, such as resetting a password, canceling a user session, deleting a user, and clearing a user’s multifactor authentication (MFA) method.
This issue has been fixed by the Windows manufacturer as of February 22, 2025, following the responsible disclosure of August 19, 2025.
Over the past few weeks, threat actors have been training their vision on websites hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances by leveraging server-side request forfary (SSRF) vulnerabilities to extract metadata information.
“EC2 instance metadata is a feature provided by AWS that allows EC2 instances to access the information they need at runtime without having to authenticate or create external API calls.” “You can publish information such as public or private IP addresses, instance IDs, IAM role credentials, and more. Many of this is sensitive data of interest to attackers.”
Source link