Innovation Platform discussed the World Nuclear Outlook report with the World Nuclear Association (WNA) and delved into its key findings and insights from them.
The World Nuclear Association has released the first World Nuclear Outlook report, providing a comprehensive analysis of international nuclear energy goals and strategies. Many countries have committed to tripling global nuclear energy capacity by 2050, as detailed in the Nuclear Energy Triplication Declaration, an ambitious plan to meet growing energy demands while significantly reducing carbon dioxide emissions around the world.
However, despite the government’s lofty ambitions, turning these goals into realistic and actionable strategies urgently requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including governments, industry leaders, investors and civil society.
Innovation Platform Editor Maddy Hall spoke with WNA’s Jonathan Cobb to dig into the report’s key findings and insights, and how, with the right strategies and frameworks in place, nuclear energy can make a significant contribution to a cleaner, safer and more sustainable energy future for everyone.
Can you provide a summary of the key facts and figures outlined in the report?
More than 30 countries have signed the Nuclear Energy Triplication Declaration, which aims to increase global nuclear capacity to approximately 1,200 GWe by 2050.
The World Nuclear Outlook report aims to collate the national policies, goals and targets set by governments for nuclear power and assess whether they are sufficient to achieve the treble target.
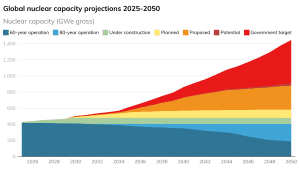
The report’s findings show that governments’ collective ambitions significantly exceed that threefold target, with a total of 1,446 GWe of nuclear capacity targeted by governments in 2050.
The report also assesses how governments can achieve their 2050 nuclear energy goals, including maximizing the contribution of reactors already in operation and those currently under construction, and implementing existing plans and proposals for new reactor construction. This could result in a total of approximately 900 GWe of operational nuclear capacity by 2050. For each country, the report identifies the gap between these measures and the nuclear energy capacity targets set by each country. Overall, approximately 300 GWe of additional nuclear capacity will be needed to meet the global treble target, and an additional 250 GWe to meet the targets set by governments.

This report examines the development and capabilities of the nuclear sector in different countries. Which countries are poised for the greatest growth? Are there significant differences in the nuclear outlook between countries, and what factors are contributing to those differences?
Five countries – China, France, India, Russia and the US – are targeting a total of nearly 1000 GWe of nuclear capacity by 2050. The United States has set the highest targets of 400GWe, China 335GWe, India 100GWe, France 89GWe, and Russia 56GWe. However, there are significant differences in how these goals are achieved, with China and the United States representing two different cases.
The United States has the largest number of nuclear reactors in operation, with a total capacity of approximately 100 GWe. Many of these reactors were built in the 1970s and 1980s, so their operation will need to be extended to maximize their contribution in 2050. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) has reviewed and approved an application to extend the operating permit from 60 years to 80 years. Plans are underway to extend the operating lives of nearly 50 nuclear reactors (about half) to 80 years to meet clean energy goals and electricity demand.
There has been little new construction in recent years, and clear plans for new reactors are limited. Achieving that capacity goal will therefore require establishing a very significant program of new nuclear construction, including establishing the supply chains needed to make this happen.
China’s intensive planning, strong state support, and well-established supply chains are enabling the expansion of nuclear energy. China has 58 GWe of operational nuclear reactors and 41 GWe under construction. Continuous new construction efforts based on repeated construction of a series of reactors result in faster and more predictable construction, with each reactor typically lasting five to six years.
China also has a clearer roadmap for future nuclear construction, with existing reactors, reactors under construction, planned and proposed reactors meeting almost the entirety of the 335 GWe target.
What factors are considered to assess and predict future nuclear power demand in different regions?
Although the report does not directly model future electricity demand, it assesses government targets and examines the underlying factors influencing nuclear demand, including population growth, transport, heating, industrial electrification, decarbonization targets, and increased electricity demand from new technologies such as data centers and digital infrastructure.
What trends does this report indicate in the development of new nuclear technologies?
The report notes that there is a trend toward greater technological diversity. While large pressurized water reactors (PWRs) remain the mainstream, small modular reactors (SMRs), microreactors, and advanced reactor designs using gas, molten salt, or liquid metal coolants are being developed. These technologies are intended to support non-electrical applications such as district heating, industrial process heat, hydrogen production, desalination, energy storage, and more flexible deployment models.
How do geopolitical factors affect the predictions made in the report? Is there a strategy for planning with these factors in mind?
The report highlights the resilience of nuclear energy to fuel supply shocks due to its high energy density and diversified uranium supply chain. Although it does not outline a formal geopolitical risk planning framework, it emphasizes supply chain diversification, life extension, and domestic capacity development as practical strategies for managing geopolitical uncertainty.
Have you encountered any challenges or unexpected discoveries while researching and writing your report?
Governments have different time horizons for their energy policy strategies. Not all companies have clear targets for specific forms of electricity generation in 2050, including nuclear. As a result, the report does not include some countries that are currently evaluating nuclear energy but have not yet set targets.
Similarly, countries already using nuclear energy may have stated some plans for future generation capacity, but not necessarily beyond 2050. Therefore, the 1,446 GWe capacity figure probably underestimates the government’s intentions for nuclear capacity in 2050.
What initiatives and policies does the report consider most important to support the expansion of nuclear energy?
The report recommends that governments integrate nuclear energy into their long-term decarbonization and energy security plans, alongside renewables and other low-carbon technologies. Durable and viable nuclear power policies and industrial strategies need to be developed to enable long-term investment and maintain industrial capacity, workforces and supply chains. We should also support life extension programs to 60-80 years, where technically possible, to avoid premature closure. In many countries, electricity markets need to be reformed to ensure fair treatment of nuclear energy alongside other low-carbon power sources and to support accelerating licensing, siting and financing mechanisms to facilitate higher construction rates.
The report recommends that financial institutions adopt technology-neutral financing and ESG policies to ensure that nuclear power and other low-carbon resources are evaluated on comparable criteria. It should also support nuclear deployment in emerging countries through financing frameworks, guarantees, and multilateral partnerships.
The report also recommends actions for the nuclear industry itself, highlighting the need to expand manufacturing and supply chain capacity, including fuel cycle infrastructure, and optimize serial production to reduce costs and shorten construction times. The nuclear industry must also prepare to meet the goals set by governments by developing large-scale deployment strategies to meet demand beyond 2035, including off-grid applications leveraging new reactor technologies.
What are the next steps and future research areas for the nuclear industry identified in the report?
Future focus areas identified include increasing construction rates, extending the operating life of nuclear reactors to 60 to 80 years, introducing advanced and small reactor technology, and expanding non-electrical uses of nuclear energy. The report also points to the need for further analysis of fuel cycle services, supply chain capabilities and financing mechanisms, particularly for deployment beyond 2035.
Finally, could you summarize WNA’s recommendations for the field as a whole?
The World Nuclear Association recommends that governments recognize nuclear energy as a central pillar of decarbonization and energy security, integrate it into long-term plans, and establish durable and implementable policies. Key recommendations include supporting life extensions, reforming electricity markets to ensure fair treatment of nuclear power, accelerating licensing and financing, and expanding industrial and supply chain capacity. If these measures are implemented, the report concludes, nuclear power can play a key role in providing safe, affordable and net-zero compatible energy by 2050.
This article will also be published in the quarterly magazine issue 25.
Source link