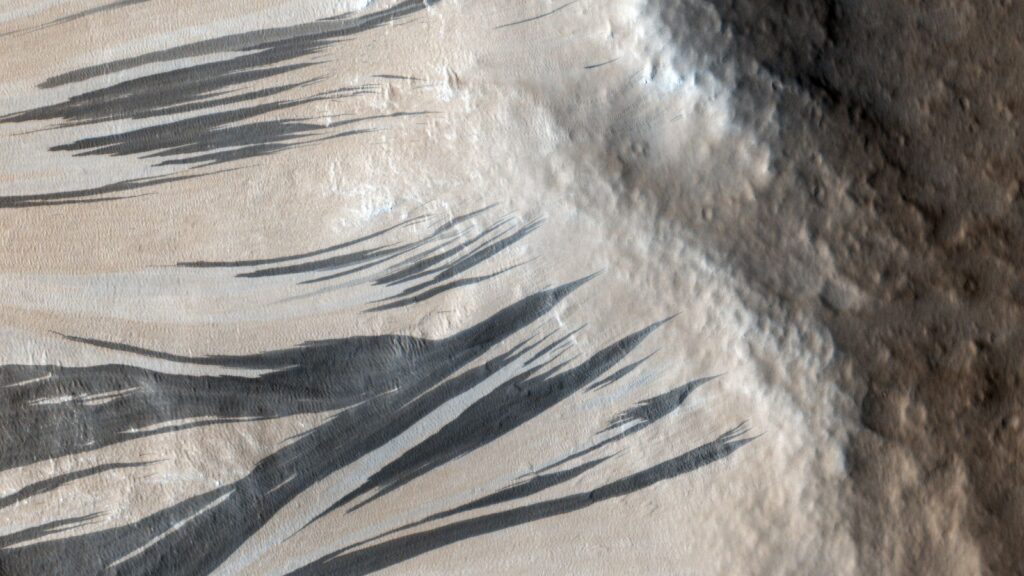
Millions of mysterious black stripes littering the surface of Mars have puzzled scientists for decades, but now researchers may finally have a good explanation. The new theory also explains why it took so long to solve this particular problem.
Mars’ “slope stripes” are dark albedo features that cover the slopes of Martian terrain. They were discovered in the 1970s, and scientists initially thought they were evidence of landslides caused by melting ice. But while scientists still think the stripes are the result of landslides, a study published in May revealed that these landslides are actually caused by a “dry process” that doesn’t involve water. This narrowed down the list of potential causes, but did not conclusively resolve the debate over the origin of the stripes.
One of the most famous examples of these stripes is on Mount Apollinaris, an extinct shield volcano located just south of Mars’ equator. Here, hundreds of parallel stripes can be seen on one side of the large ridge, giving the structure a “barcode-like” appearance (see below). These stripes appeared sometime between 2013 and 2017, and scientists later realized they were the result of a nearby meteorite impact, Live Science’s sister site Space.com reported.
you may like
As a result, some researchers have speculated that other seismic phenomena, such as meteorite impacts or fire earthquakes, are responsible for most slope stripes. But a new study published in the journal Nature Communications on November 6 suggests that this is not the case.
Instead, an analysis of some 2.1 million slope stripes photographed by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter between 2006 and 2024 reveals that nearly all new stripes are the result of erosion by seasonal winds and dust. (The study estimates the total number of Martian oblique stripes to be about 1.6 million, but some stripes were included in more than one image set.)
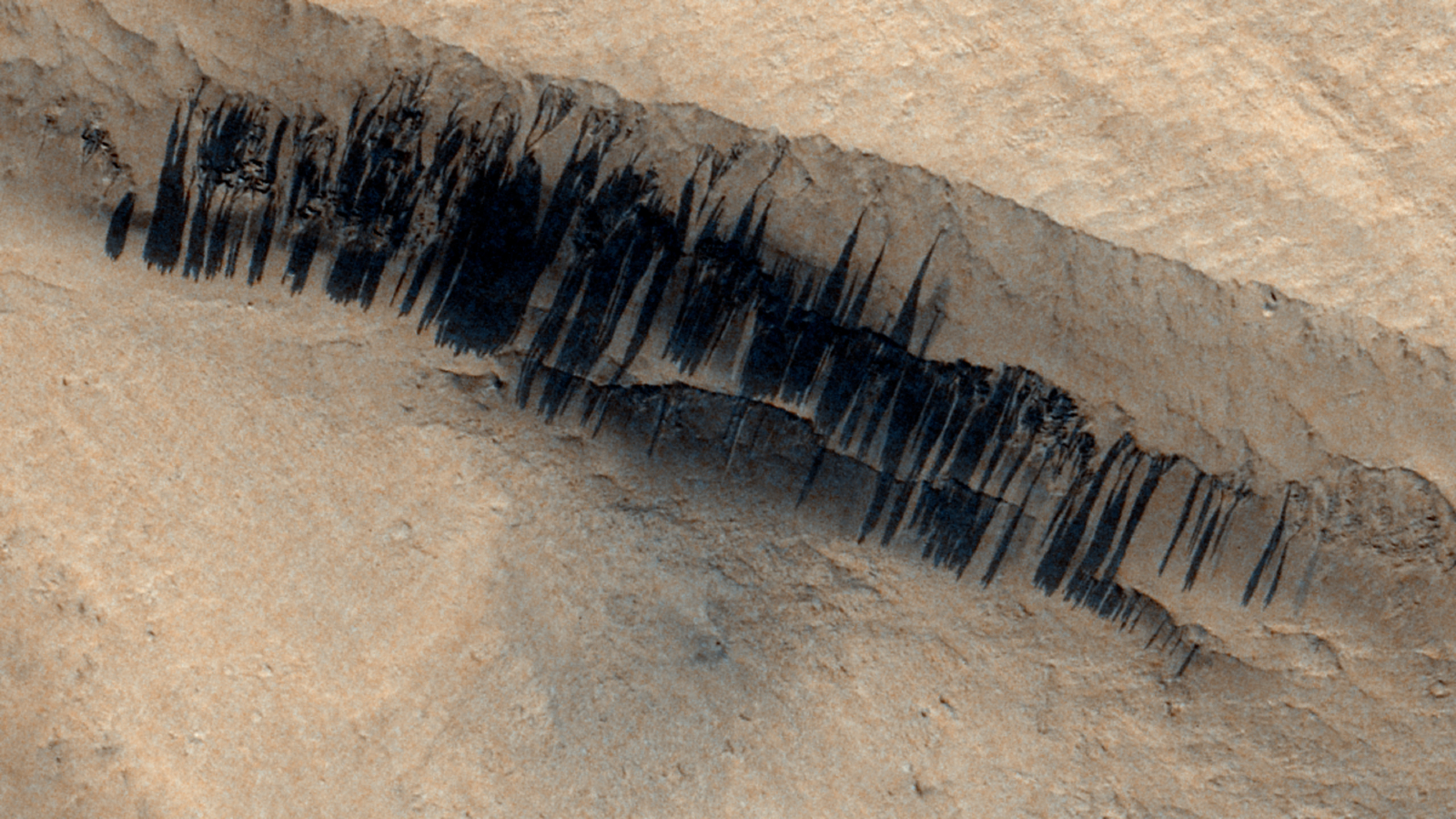

“Dust, wind and sand dynamics appear to be the main seasonal factors in the formation of slope stripes,” study sole author Valentin Bickel, a planetary scientist at the University of Bern in Switzerland and co-author of the May study, said in a statement. “Meteor strikes and earthquakes appear to be locally distinct, but on a global scale they are relatively unimportant factors. [of streak formation]” he added.
Bickel estimates that less than 0.1% of the newly formed slope stripes were caused by meteor impacts or Mars earthquakes.
Bickel’s analysis found that slope stripes are divided into five major regions across Mars, and new stripes form in each of these regions when seasonal wind speeds are highest and exceed a threshold for “dust movement.” Beyond this threshold, landslides can occur more easily in the area, Bickel added.
This process is similar to strong winds kicking up Martian dust and creating giant tornadoes, or “dust devils,” across the planet’s vast plains.
Perhaps the reason it took scientists so long to solve this puzzle is because it’s all happening in the dark. “The conditions most likely for seasonal stripe formation appear to occur at sunrise and sunset, explaining the lack of direct observations of stripe-forming events to date,” Professor Bickel said in the study.
The study also revealed that the formation of diagonal stripes is likely to occur at an annual rate of about 0.05 new stripes per existing stripe. Given that there are an estimated 1.6 million slope stripes, this means that the current rate of new stripe formation is about 80,000 per year. Most streaks can last decades before disappearing, but we don’t have enough orbital data to tell for sure.
Slope stripes cover less than 0.1% of Mars’ surface, but a new study suggests they may be the largest source of dust in the atmosphere. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the role of streaks in the Martian dust circulation may have implications for future human colonization of Mars and should be an important goal for future Mars missions.
“These observations could lead to a deeper understanding of what is happening on Mars today,” Colin Wilson, project scientist for the European Space Agency’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, who was not involved in the new study, said in a statement. “Obtaining long-term, continuous global observations that reveal a dynamic Mars is a key objective for current and future orbiting spacecraft.”
Source link

