Cybersecurity researchers have discovered five vulnerabilities in Fluent Bit, an open-source lightweight telemetry agent. These can cascade to compromise and take over cloud infrastructure.
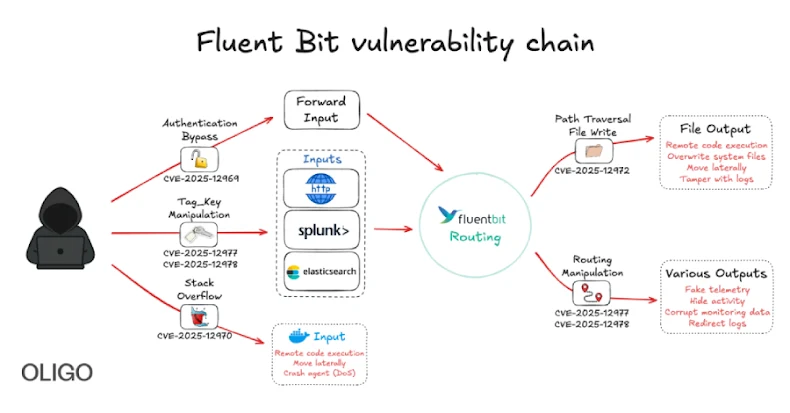
Oligo Security said in a report shared with The Hacker News that the security flaw “allows an attacker to bypass authentication, perform path traversal, remotely execute code, cause a denial of service condition, and manipulate tags.”

Successful exploitation of this flaw could allow attackers to disrupt cloud services, manipulate data, and penetrate deeper into cloud and Kubernetes infrastructure. The list of identified vulnerabilities is as follows:
CVE-2025-12972 – Path traversal vulnerability due to use of unsanitized tag values to generate output file names. This allows the attacker to write or overwrite arbitrary files on disk, allowing for log tampering and remote code execution. CVE-2025-12970 – A stack buffer overflow vulnerability in the Docker Metrics input plugin (in_docker) could allow an attacker to create a container with an overly long name to trigger code execution or crash the agent. CVE-2025-12978 – A vulnerability in the tag matching logic allows an attacker to spoof the trusted tag assigned to all events ingested by Fluent Bit by guessing only the first character of the Tag_Key, allowing the attacker to reroute logs, bypass filters, and inject malicious or misleading records under the trusted tag. CVE-2025-12977 – Improper input validation for tags derived from user control fields allows attackers to insert line breaks, traversal sequences, and control characters that can corrupt downstream logs. CVE-2025-12969 – Missing security.users authentication in the in_forward plugin, which is used to receive logs from other Fluent Bit instances using the Forward protocol, allows attackers to send logs, inject fake telemetry, and flood security products’ logs with bogus events.
“The amount of control allowed by this class of vulnerabilities allows attackers to penetrate deeper into cloud environments and use Fluent Bit “It may be possible to execute malicious code via an attacker, while dictating which events are logged, erasing or rewriting incriminating entries to cover their tracks after an attack, or injecting fake telemetry or plausibly false events to mislead responders,” the researchers said.
The CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) said in an independent advisory that many of these vulnerabilities require an attacker to have network access to the Fluent Bit instance, adding that they could be used for authentication bypass, remote code execution, service interruption, and tag manipulation.
Following responsible disclosure, this issue was resolved in versions 4.1.1 and 4.0.12 released last month. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is also engaging in coordinated disclosure, urging customers running Fluentbit to update to the latest version for optimal protection.

Given Fluent Bit’s popularity within corporate environments, this shortcoming could compromise access to cloud services, allow data tampering, and take control of the logging service itself.
Other recommended actions include avoiding the use of dynamic tags for routing, locking down output paths and destinations to prevent tag-based path expansion or traversal, mounting /fluent-bit/etc/ and configuration files as read-only to block runtime tampering, and running services as a non-root user.
This development comes more than a year after Tenable detailed a flaw in Fluent Bit’s built-in HTTP server (CVE-2024-4323 aka Linguistic Lumberjack) that, if exploited, could lead to a denial of service (DoS), information disclosure, or remote code execution.
Source link