Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered that a previously undocumented threat actor known as TA585 has been observed distributing off-the-shelf malware called MonsterV2 through phishing campaigns.
The Proofpoint Threat Research team described this cluster of threat activity as sophisticated, leveraging web injections and filtering checks as part of the attack chain.
“TA585 is noteworthy because it appears to possess the entire attack chain using multiple delivery techniques,” said researchers Kyle Cucci, Tommy Magyar, and Selena Larson. “Instead of relying on other threat actors, such as paying distribution fees, purchasing access from an initial access broker, or using third-party traffic delivery systems, TA585 manages its own infrastructure, distribution, and malware installation.”
MonsterV2 is a remote access Trojan (RAT), stealer, and loader that Proofpoint first observed being advertised on criminal forums in February 2025. It’s worth noting that MonsterV2 is also known as Aurotun Stealer (a misspelling of “autorun”) and was previously distributed via CastleLoader (aka CastleBot).

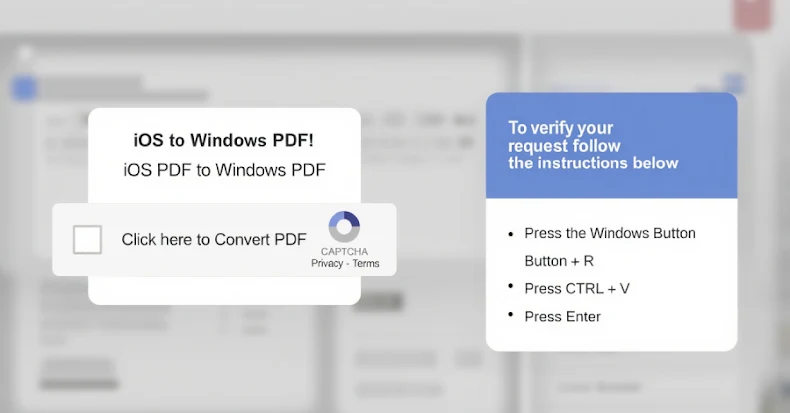
Phishing campaigns distributing this malware use Internal Revenue Service (IRS)-themed decoys to trick users into clicking a fake URL that leads to a PDF, which then links to a web page that employs ClickFix social engineering tactics to[ファイル名を指定して実行]It has been observed to activate infections by running malicious commands in dialogs or PowerShell terminals. PowerShell commands are designed to run PowerShell scripts for the next stage of deploying MonsterV2.
A subsequent wave of attacks detected in April 2025 relied on malicious JavaScript injection into legitimate websites that provided fake CAPTCHA validation overlays to launch attacks via ClickFix and ultimately lead to malware delivery via PowerShell commands.
The first iteration of this campaign distributed the Lumma Stealer before TA585 switched to MonsterV2 in early 2025. Interestingly, JavaScript injection and related infrastructure (intlspring)[.]com) is also linked to the Rhadamanthys Stealer distribution.
In the third campaign run by TA585, tagging a GitHub user with a fake security notification containing a URL that leads to an attacker-controlled website triggers an email notification from GitHub.
Both activity clusters centered around web injects and fake GitHub alerts are associated with CoreSecThree. According to PRODAFT, CoreSecThree is a “sophisticated framework” that is known to be active since February 2022 and is “consistently” used to propagate stealer malware.

MonsterV2 is a full-featured malware that can steal sensitive data, act as a clipper by replacing cryptocurrency addresses in the infected system’s clipboard with wallet addresses provided by threat actors, establish remote control using Hidden Virtual Network Computing (HVNC), receive and execute commands from external servers, and download additional payloads.
The malware is being sold by Russian-speaking attackers for $800 per month for the “Standard” edition, while the “Enterprise” version, which comes with a stealer, loader, HVNC, and Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP) support, costs $2,000 per month. What’s remarkable about this stealer is that it avoids infecting Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries.
MonsterV2 is typically packed using a C++ encryption tool called SonicCrypt, which allows it to evade detection by running a series of anti-analysis checks before decrypting and loading the payload.
Once launched, the malware not only escalates its privileges, but also decrypts and resolves Windows API functions essential to its functionality. It then decodes the embedded configuration and connects to a command-and-control (C2) server to determine its next course of action based on the configured parameters.
anti_dbg, when set to True, the malware will try to detect and avoid the debugger in use anti_sandbox, when set to True, the malware will try to detect the sandbox and run some rudimentary anti-sandbox techniques aurotun (this misspelling gave it the name Aurotun Stealer). If set to True, the malware will attempt to set persistence on the host If priviledge_escalation is set to True, the malware will attempt to escalate privileges.

Once the malware successfully establishes a connection with the C2 server, it sends a request to ‘api.ipify’ to send basic system information and system geolocation information.[.]org.” The response from the server contains a command to be executed on the host. Some of the supported features are listed below.
Execute infostealer functions and extract data to the server Execute arbitrary commands via cmd.exe or PowerShell Terminate, pause, or resume the target process Establish an HVNC connection to the infected system Take a screenshot of the desktop Start a keylogger Enumerate, manipulate, copy, or extract files Shut down or crash the system Download and execute next-stage payloads such as StealC Remkos RAT
“However, this activity was not correlated with TA585. Specifically, in the case of StealC, the MonsterV2 payload was configured to use the same C2 server as the dropped StealC payload,” Proofpoint said. “TA585 is a unique adversary with advanced targeting and delivery capabilities. As the cybercrime threat landscape is constantly changing, TA585 employs effective strategies for filtering, delivery, and malware installation.”
Source link