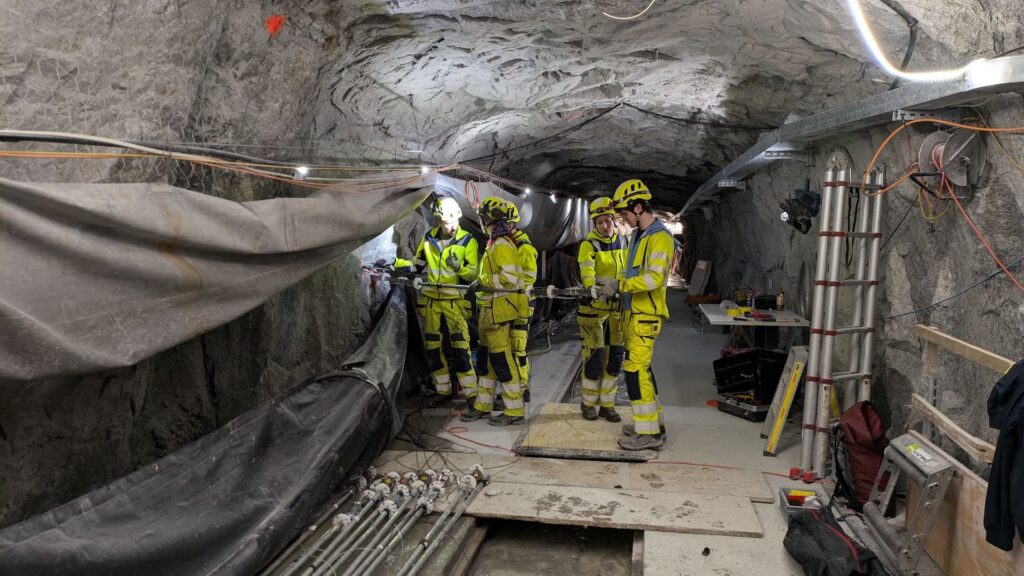
Scientists are intentionally triggering earthquakes from tunnels deep underground in the Alps. It may sound like something out of a James Bond movie, but the goal isn’t chaos or destruction. Rather, researchers with the Fault Activation and Earthquake Eruption (FEAR) project are looking for ways to determine the risk of an earthquake before it occurs.
Despite increasing monitoring of faults around the world, researchers still do not understand the immediate triggers of earthquakes. We also don’t know what causes some ruptures to occur on short stretches of fault lines, while others occur over many miles, causing larger ruptures. Domenico Giardini, professor of seismology and geodynamics at ETH Zurich, told Live Science that for now, geoscientists are limited to studying these phenomena only after they occur.
you may like
This means placing thousands of monitors on the fault and triggering an actual earthquake under controlled conditions, which is not an easy prospect. But Giardini and his colleagues are harnessing the enormous power of the Alps themselves. There are deep fault lines in these mountains on the border of Switzerland and Italy. The zigzag network of cracks beneath it is the legacy of millions of years of tectonic movements. The compressive force of the towering mountains alone is enough to fracture rock 0.6 to 1.2 miles (1 to 2 kilometers) below the surface.
Rocks on the sides of these faults sometimes slip, causing mainly small earthquakes. Using existing tunnels once used to build railroad projects, the FEAR project approaches one of these faults and pumps water into it to generate earthquakes on a convenient schedule.
“In the history of the Alps, sooner or later something like this will happen, and we are making sure it happens next week,” Giardini said.
This process is similar to what happens when oil and gas companies inject wastewater through wells into fault areas such as Oklahoma or Texas. This water lubricates the fault and reduces the friction required for fault rupture.
The difference is that Giardini and his team have a dense network of seismometers and accelerometers directly above the fault, so they can precisely measure how the fault moves in response to this reduction in friction. The research team has already triggered hundreds of thousands of earthquakes up to magnitude zero. (Earthquakes are measured on a nonlinear logarithmic scale, so very small earthquakes with a magnitude of 0 or negative can occur.)
Next week, researchers plan to begin injecting hot water into the fault to see how temperature affects earthquake development. And Giardini said it will start producing earthquakes up to magnitude 1 in March.
The idea is that if we can figure out what parameters cause an earthquake of a certain size – in essence, if we can cause an earthquake of the size we want – we will eventually be able to measure dangerous faults in the real world before they rupture and calculate the kinds of stresses needed to cause an earthquake of a certain size on that fault.
“years ago [in February 2023]”There was a very strong earthquake on the Syrian-Turkish border,” Giardini said. “We know that the fault continues south and north.” We want to understand whether the next earthquake will be a magnitude 7, a magnitude 8, or a magnitude 8.5. ”
He said certain parameters have already been shown to be important, such as the amount of strain in the rocks outside the fault. Researchers are also beginning to understand how earthquakes jump from one fault to an adjacent fault.
“We’re looking at examples of self-produced cells underground that are very similar to what happens in nature,” Giardini said.
Source link

