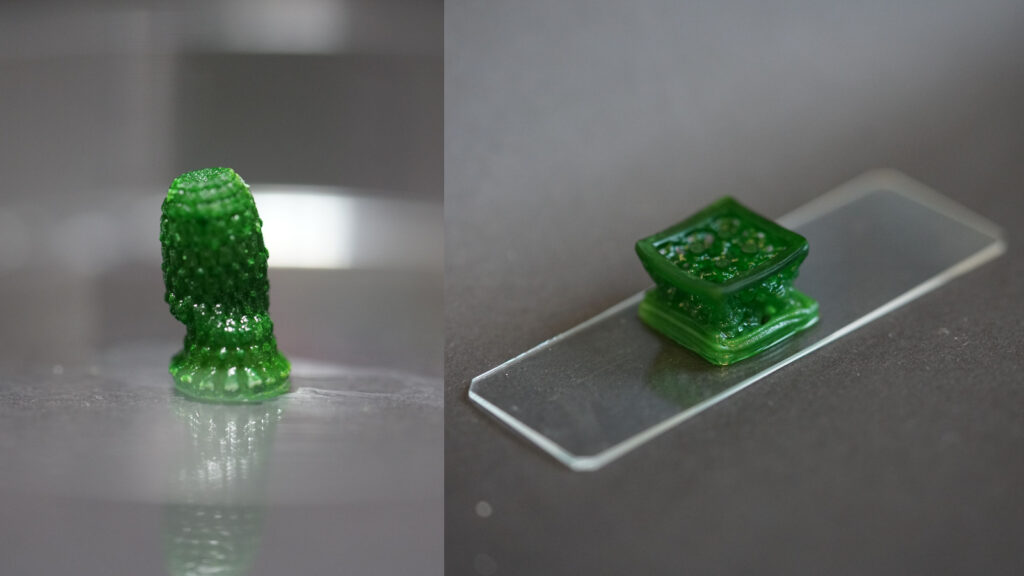
Swiss scientists have created new “living” materials, including blue-green algae, which they say can be used in buildings one day to combat climate change.
Thanks to blue-green algae, or cyanobacteria, the new material is photosynthesis. This means that carbon dioxide (CO2), sunlight and water can be chemically converted to oxygen and sugar, which promotes growth.
In the presence of certain nutrients, the material can also convert CO2 into solid carbonate minerals such as limestone, researchers said in a new study published April 23 in the journal Nature Communications. Over time, these minerals build robust lattices inside the material, strengthening it, and store carbon in a more stable form than photosynthesis.
You might like it
“The material can preserve carbon not only in biomass, but also in the form of minerals, a special property of these cyanobacteria,” said Mark Tibbitt, an associate professor of polymer engineering at Zurich, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH), Zurich, in a statement. “As a building material, it will help to store CO2 directly in the building in the future.”
Without the ability to sequester carbon in mineral form, the new material will be floppy and jelly-like. However, by producing mineral skeletons with CO2 and nutrients, this material gradually increases its own mechanical strength, and according to research it becomes a good candidate for construction.
Researchers suggest that the material can be used as a coating for facade buildings to suck CO2 directly from the atmosphere. In this study, the material isolated CO2 continuously for 400 days and stored approximately 26 milligrams of CO2 per gram in the form of carbonate precipitates. The rate is very efficient and is significantly higher than other forms of biological CO2 sequestration, the researchers said.
Related: The new mysterious material designed by AI is as light as foam, but as strong as steel
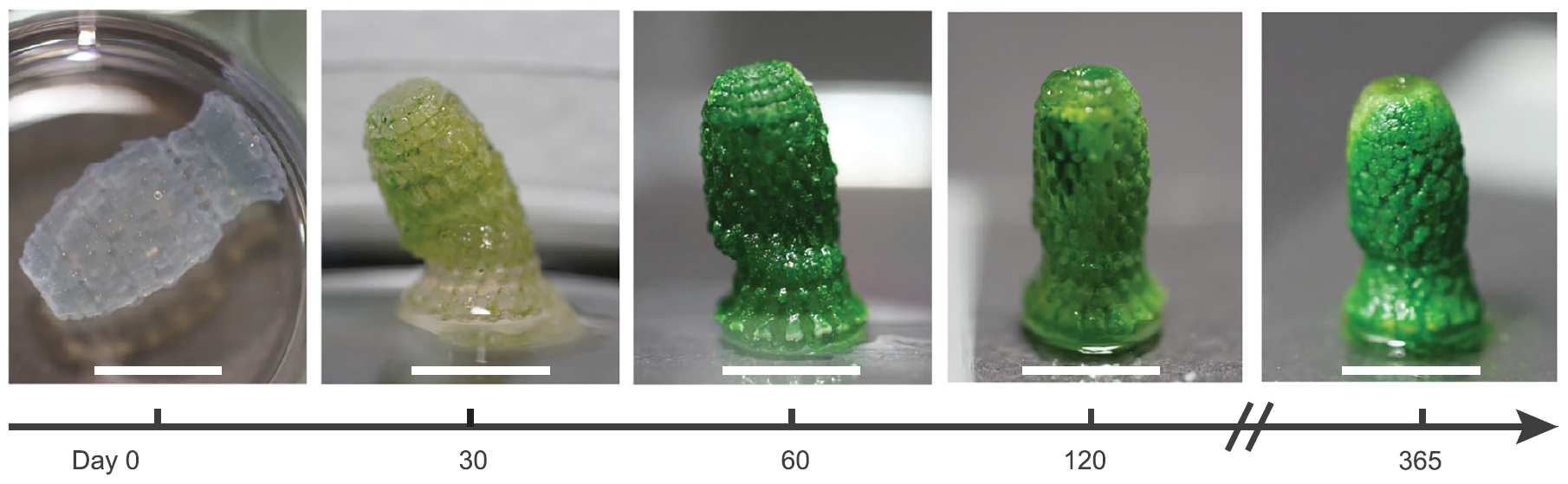
The increasingly bright green color of the material is evidence that it preserves CO2 in the form of biomass. However, cyanobacteria can only grow that much, and studies have shown that the rate at which carbon was stored in water-grade cells was leveled after about 30 days. This means that carbon sequestration in the form of biomass decreases beyond this time frame, but does not stop.
The base of the new material is a 3D printable hydrogel. In other words, it is a gel with a high amount of moisture, made from crosslinked molecules. Researchers chose porous hydrogels, growing cyanobacteria within them, allowing sufficient light, water and CO2 to penetrate the gel and reach the bacteria. Scientists then tested hydrogels of various shapes to determine the best geometry for the survival of cyanobacteria.
“Cyanobacteria are one of the oldest living organisms in the world,” said research co-authors of Yifan Cui, a doctoral student in polymer engineering at ETH Zurich, in a statement. “They are very efficient in photosynthesis and even the weakest light can be utilized to generate biomass from CO2 and water.”
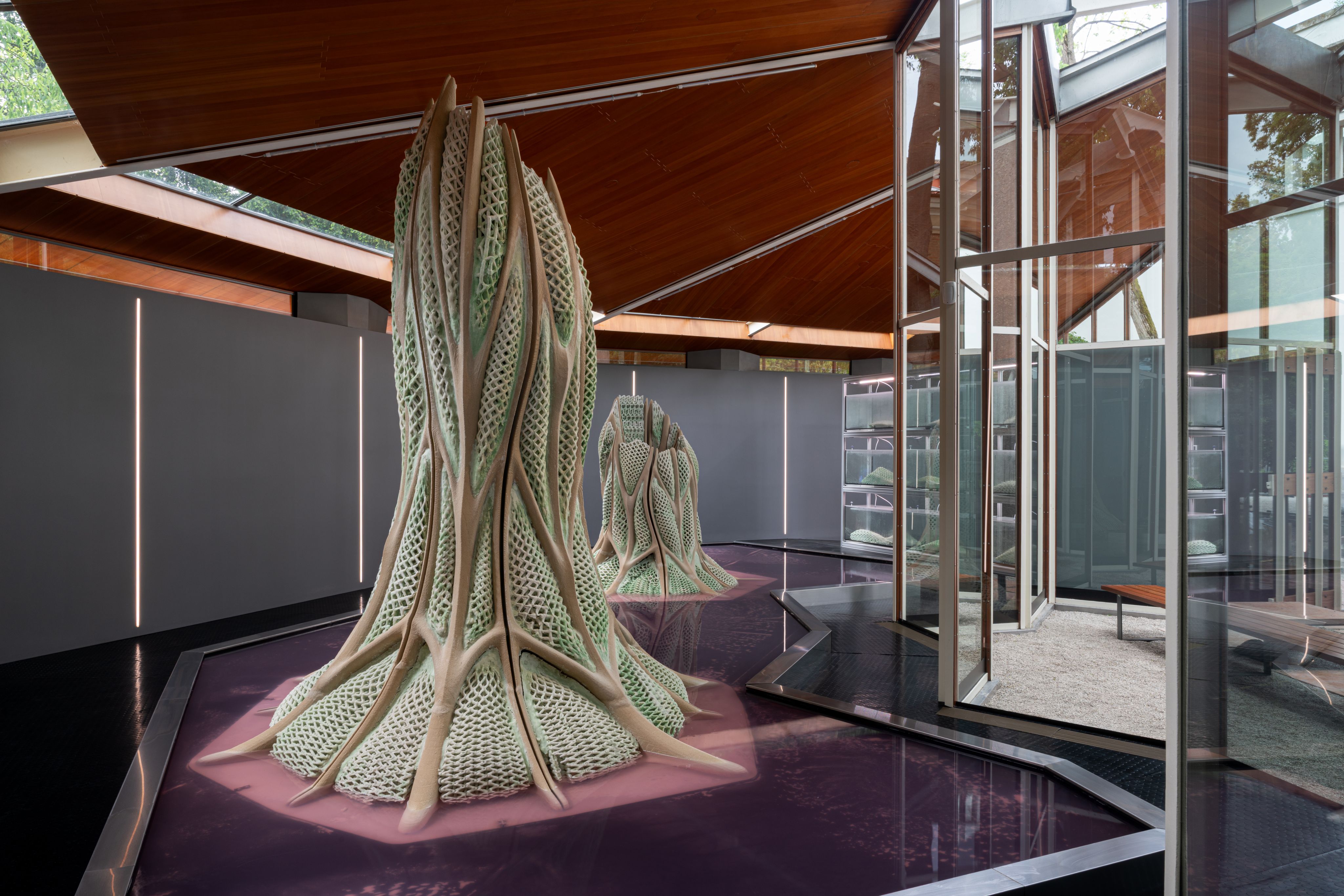

In this study, the researchers soaked hydrogels in artificial seawater and provided the nutrients needed for mineral precipitation. Further research is needed to determine how calcium-containing nutrients containing magnesium can be injected into the material if they coat the building.
In the meantime, researchers dream of the various shapes that materials can take. At the architecture exhibition held in Venice, the team presented the material in the form of objects, each of which can absorb up to 40 pounds (18 kilograms) of CO2 per year, or two tree trunks, which can absorb 20-year-old pine trees, according to a statement.
Researchers mentioned in the study may be able to increase photosynthesis rate before embedding cyanobacteria into the material, genetically, before embedding them in the material.
“We consider our living materials to be a low-energy and environmentally friendly approach that can combine CO2 from the atmosphere and complement existing chemical processes for carbon sequestration,” Tibbitt said.
Source link