New simulations reveal that if the infamous “urban killer” asteroid 2024 YR4 hits the moon in seven years, it could potentially shower the Earth with “bullet-like” fragments, causing an eye-catching meteor shower, putting satellites orbiting the planet in danger.
The 2024 YR4 is a potentially dangerous asteroid about 200 feet (60 meters) wide, large enough to wipe out large urban areas when pounded directly on the Earth. It was first discovered in December 2024, but made headlines earlier this year when scientists first predicted that they could collide with Earth on December 22, 2032. The probability of a collision peaked at 3.1% in February. However, subsequent analysis revealed that there is no chance that it would affect our planet.
However, in April, researchers realized that while Earth is no longer on the fire line, space rocks could still hit the moon. The probability of such a conflict has grown slowly and steadily, and recently jumped to 4.3% earlier this month. Experts will know the ultimate potential by 2028 when asteroids will take the next close approach to our planet.
You might like it
In a new study uploaded to the preprint server ARXIV on June 12, researchers ran computer simulations to model what the effects of the moon would look like. The team estimated that up to 220 million pounds (100 million kilograms) of material could be emitted from the moon. If the 2024 YR4 hits the globe-facing side of the moon (almost 50/50 chance), 10% of this fragment could be drawn into by Earth’s gravity the next day, scientists write.
The 2024 YR4 will be the largest space rock to hit the moon in “at least five,000 years,” an expert on solar system dynamics at Western University of Ontario, Canada. The impact “is comparable to a massive nuclear explosion in terms of the amount of energy released,” he added.
Related: “Only the tip of the iceberg”: Why dangerous asteroids like 2024 have plagued the Earth for decades
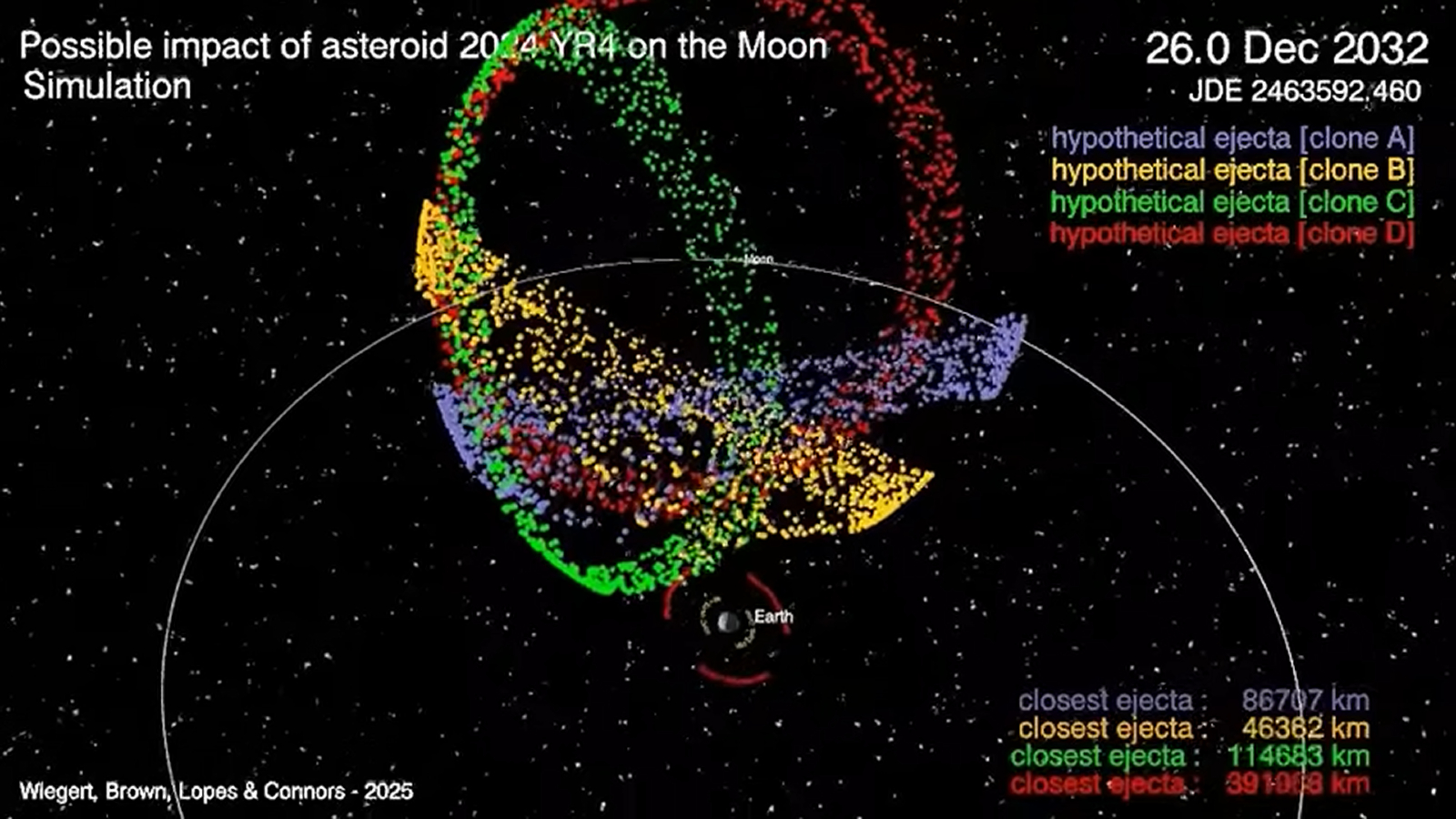
It is important to note that a new simulation (shown below) was created before the probability of a moon impact rose from 3.8% to 4.3% on June 16th. But that’s still far from certainty. The results of new research have not yet been peer-reviewed.
It is unlikely that any of the potential fragments poses a risk to people on Earth. Instead, we might be treated to a “magnificent” meteor shower, where selfish fragments of rock continue for several days in the Earth’s atmosphere and are visible to people all over the world, Weigart said.
But while we are almost certainly safe on the ground from potential lunar meteor showers, space-based infrastructure can be threatened. The amount of debris that can pull close to Earth could make our satellite about 1,000 times more likely to be hit by a meteor. And by 2032, the number of spacecraft orbiting our planet is expected to rise significantly.
“Centimeter-sized rocks that travel at tens of thousands of meters per second are very similar to bullets,” Weigart said. Such objects can easily remove satellites or cause serious damage to human-existing space stations, such as Tiangon Station in China. (The International Space Station is scheduled to be discontinued by 2030.)

If the possibility of lunar impact increases further in the coming years, government agencies may decide to divert the asteroid course to protect Earth’s space assets. Asteroids are “good targets” to test our planetary defense capabilities, Weigart said. “I’m sure that’s going to be considered.”
NASA has already demonstrated its ability to redirect dangerous asteroids in 2022. This is when you decouple the asteroid’s dimorphos trajectory by hitting the DART probe. The 2024 YR4 is about half the size of that particular space lock.
But trying to change the trajectory of the Spacelock can be “dangerous” if you wait too long, the wrong movement can put it on a devastating collision course with the Earth, Weigart said.
Some experts are worried that the Trump administration’s proposal for NASA’s budget will make it difficult to track dangerous asteroids such as the 2024 YR4 in the future.
Source link

