Scientists have created the first significant Meteloite diamond, also known as Lonsdelaite or hexagonal diamonds.
Scientists reported on July 30th in Nature magazine on July 30th, with high-pressure technology that created the ultra-hard diamond small disc, which could ultimately replace the ultra-hard diamond with applications such as drilling tools and electronics.
Diamonds hold a record of the world’s most difficult naturally occurring substances. Each carbon atom in the infinitely repeated molecular structure forms four equal layer bonds on the other carbon atoms, each separated at an angle of 109.5 degrees, creating an infinite array of complete tetrahedra. From the side, this structure appears to contain three repeating carbon atoms (labeled as a, b, c). This results in diamonds that what crystallologists call face-centered cubic crystal structures.
You might like it
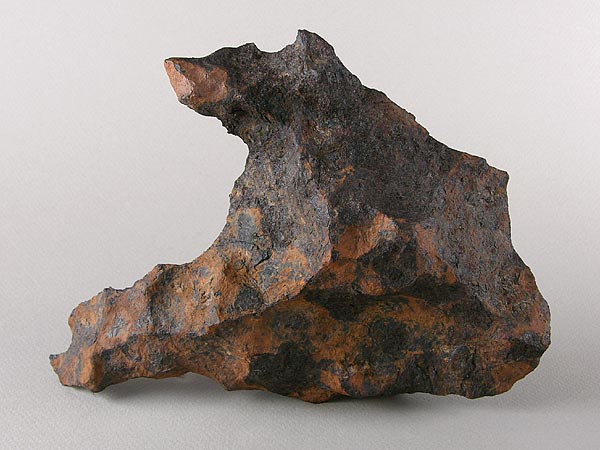
However, in the 1960s, subtle differences in diamond structures were proposed. The small impure crystals of this structure were later discovered in Canyon Diablo Met stones and crashed in the Arizona Desert 50,000 years ago.
Unlike cubic diamonds, this form contains two different bond lengths. One is slightly longer than a regular diamond, and the other is a little shorter. The carbon atoms are still organized in the infinite plane of tetrahedra. However, this time, when viewed from the side, the structure only contains two repeating layers (labeled a and b). This slight shift in the carbon layer gives the metstone diamond a hexagonal structure. Scientists should increase the hardness of solids by 58%.
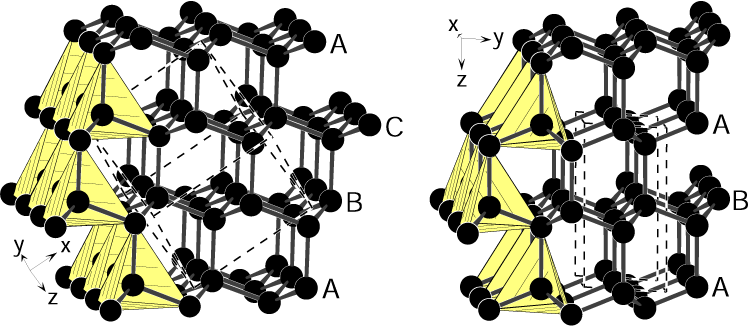
However, it was difficult to prepare a sample of this hexagonal structure large enough to analyze. Furthermore, the presence of other contaminated carbon in the original metstone samples, such as graphite, cubic diamonds, and amorphous carbon, led to doubt whether there were any hexagonal diamonds at all.
Related: Why do diamonds come in different colors?
Inspired by the meteor fragments of Canyon Diablo, Wenzhiyan and colleagues at the High-Pressure Science and Technology Advanced Research Center in Beijing tried to replicate the lab’s shocking and intense conditions with Earth and develop high-pressure, high-temperature synthesis using diamond anvil cells. From purified graphite starting from another form of carbon, they slowly and carefully compressed the material, and the shifted atoms were fixed with target heat from the laser.

“At a pressure of approximately 20 GPA (200,000 atmospheres), a flat carbon layer of graphite is forced to slide and bond with adjacent layers, forming the profitable carbon honeycomb characteristic of hexagonal diamonds.” “Laser heating above 1400°C [2,552 Fahrenheit] Once these distorted hexagonal diamond tetrahedra formed, the team slowly released pressure, preventing new crystals from returning naturally to graphite.
The team then used powerful techniques to display the crystal structure and confirm the results. The crystal disks remained somewhat impure, but those containing random fragments of cubic diamonds revealed that electron microscope images clearly showed its AB carbon layer, and X-ray crystallography revealed hexagonal structures.
“This is a good first demonstration,” said Sumen Mandal, a physicist who specializes in the application of diamonds at Cardiff University in the UK. “Now we need pure crystals and more materials to begin to explore its physical and mechanical properties, its thermal properties, its electrical properties, all of this.”
Research shows that hardness testing generally requires a larger sample than that produced by Yang’s team. But they have confirmed that it is at least as strict as the regular diamond sul.
The team hopes to finally start replacing traditional diamonds with hexagonal diamonds in industrial technologies such as precision machinery, high performance electronics, quantum technology, and thermal management systems, but such applications are still 10 years away.
“Looking forward, our goal is to produce larger, higher quality hexagonal diamond samples suitable for real-world applications,” he said. “These efforts will help adjust the properties of hexagonal diamonds for specific applications and pave the way for industrial adoption.”
Source link

