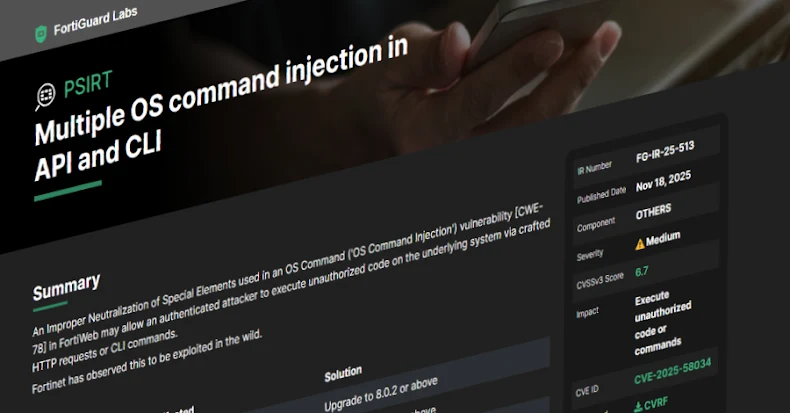
Fortinet has warned that a new security flaw exists and is being exploited in FortiWeb.
This medium severity vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-58034, has a CVSS score of 6.7 out of a maximum of 10.0.
“Improper Disabling of Special Elements Used in OS Commands (“OS Command Injection”) Vulnerability” [CWE-78] “FortiWeb could allow an authenticated attacker to execute malicious code on the underlying system via a crafted HTTP request or CLI command,” the company said in an advisory Tuesday.
This means that for a successful attack, the attacker must first authenticate themselves through other means and chain that with CVE-2025-58034 to execute arbitrary operating system commands.

This issue has been resolved in the following versions:
FortiWeb 8.0.0 to 8.0.1 (upgrade to 8.0.2 or later) FortiWeb 7.6.0 to 7.6.5 (upgrade to 7.6.6 or later) FortiWeb 7.4.0 to 7.4.10 (upgrade to 7.4.11 or later) FortiWeb 7.2.0 to 7.2.11 (upgrade to 7.2.12) FortiWeb 7.0.0 – 7.0.11 (upgrade to 7.0.12 or later)
The company praised Trend Micro researcher Jason McFaddin for reporting the flaw under its responsible disclosure policy.
Interestingly, this development comes just days after Fortinet confirmed it had silently patched another critical FortiWeb vulnerability in version 8.0.2 (CVE-2025-64446, CVSS score: 9.1).
“As soon as we learned of this issue, we began PSIRT response and remediation efforts, which are ongoing,” a Fortinet spokesperson told Hacker News. “Fortinet diligently balances our commitment to customer security with a culture of responsible transparency.”
It is unclear at this time why Fortinet chose to patch the flaw without releasing an advisory. However, this move puts defenders in a disadvantageous position and effectively prevents them from responding appropriately.
“When popular technology vendors fail to communicate new security issues, they are issuing an invitation to attackers while choosing to block the same information from defenders,” VulnCheck noted last week.
Source link