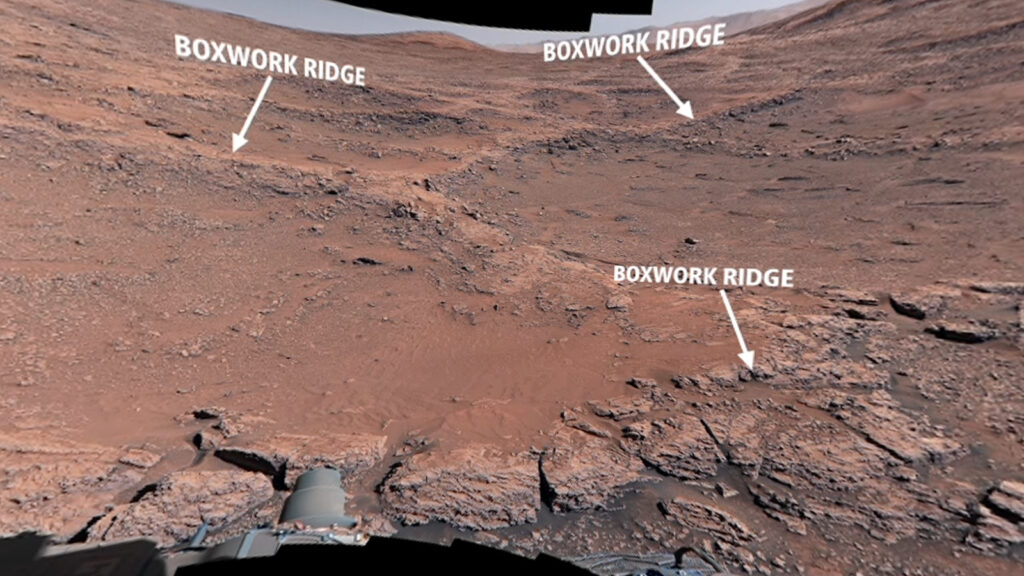
NASA’s curiosity Mars Rover took the first close-up image of the giant Mars “Spiderwebs” on the red planet. The zigzag ridges left in ancient groundwater can reveal more about Mars’ watery past and provide clues as to whether the planet once held extraterrestrial life, researchers say.
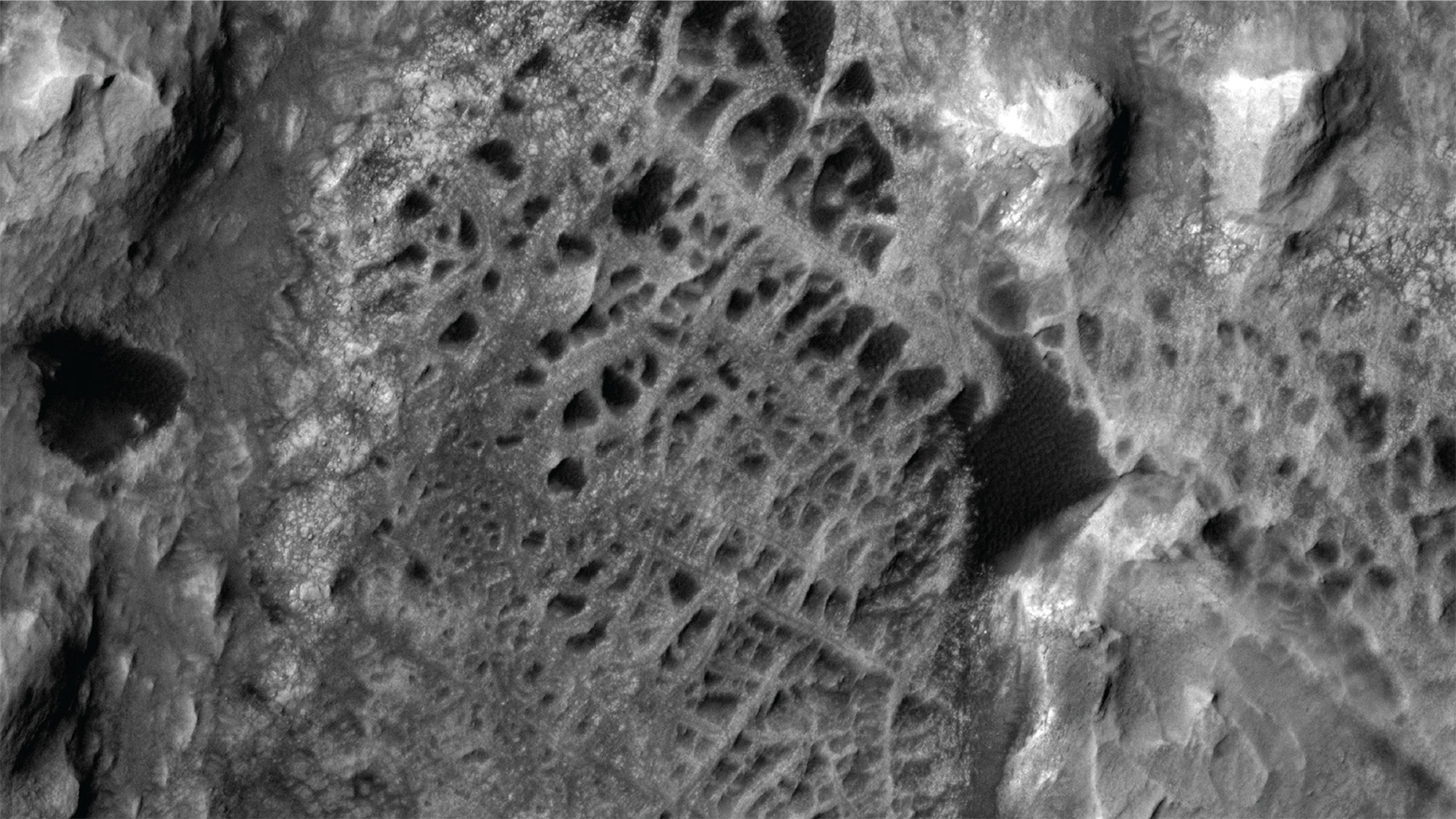
Web-like features known as “boxwork” consist of mineral-rich rock sequestration ridges that rarely litter the surface of Mars. The pattern extends up to 12 miles (20 km) and appears to have been rotated by a giant arcnid when viewed from space. However, up until now, these structures have not been studied up close.
The formation of small boxes is found in cave walls on Earth and is formed through mechanisms similar to stone lags and largs. Scientists suggest that the same mechanism created these structures on Mars, only on much larger scales.
You might like it
“The bedrock below these ridges likely formed when groundwater drips through rocks that have accumulated, hardened and left minerals that become cement-like,” a NASA representative wrote in a statement. “We used up rocks for years of Martian wind sandblasting, but we revealed a network of resistant ridges, not minerals.”
Web-like features should not be confused with the infamous “Mars spider.” This is a geological feature created by carbon dioxide ice on Earth, and has recently been reproduced on Earth for the first time.
Related: 32 things on Mars that don’t seem to be there

Curiosity is currently exploring a patch of boxwork on a 3.4-mile (5.5 km) slope in the heart of Gale Crater, where the wandering robot landed in 2012. The rover departed in November 2024 and arrived earlier this month. The feature is that the priority target for mission scientists is that no ridges appear anywhere else above the mountain. Experts don’t know why.
On June 23rd, NASA released its first close-up image of Faux SpiderWebs and released an interactive video (see below) on its YouTube channel. This allows you to explore 3D sites.
Rover also excavated and analyzed several samples of rock surrounding web-like ridges, and found that they contained veins of calcium sulfate, a salty mineral left behind by groundwater. This particular mineral has not been seen in Mount Sharp before, so the discovery here is “really surprising.”

Please take a look
Researchers hope that by studying boxwork nearby, they can learn more about Mars’ watery past before Earth’s oceans are stripped of by solar radiation. Future findings could also shed light on the huge underground oceans recently discovered beneath the Martian crust.
Some experts believe the ridge can help resolve the debate about whether Mars once held extraterrestrial life.
“These ridges contain underground crystallized minerals, where warm, salty liquid water has flowed,” says Kirstensibach, a Curiosity Mission Scientist at Rice University in Houston, who previously studied the area. “Early Earth microbes may have survived in similar environments, which makes this an exciting place to explore.”
Mars Quiz: Do you have any knowledge about the Red Planets from this world?
Source link