On January 11, 2026, I watched anxiously at California’s tightly controlled Vandenberg Space Force Base as an awe-inspiring SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifted NASA’s new exoplanet telescope, Pandora, into orbit.
Exoplanets are worlds orbiting other stars. From Earth, they are very difficult to observe because they appear as very dark spots right next to their host star, millions to billions of times brighter and drowning out the light reflected from the planet. The Pandora telescope will join and complement NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in studying these distant planets and the stars they orbit.
I’m a professor of astronomy at the University of Arizona, specializing in the study of planets around other stars and astrobiology. I am a Pandora collaborator and lead the Exoplanet Science Working Group. We built Pandora to break down the barriers that limit our ability to study small exoplanets in detail and search for life there: to understand and remove sources of noise in our data.
you may like
Observation of exoplanets
Astronomers have a knack for studying the atmospheres of exoplanets. By observing planets orbiting in front of their host star, we can study starlight passing through the atmosphere.
Observing these planetary transits is similar to holding a glass of red wine over a candle. The light that shines through reveals the fine details that reveal the quality of the wine. By analyzing starlight filtered through a planet’s atmosphere, astronomers can find evidence of water vapor, hydrogen, clouds, and even look for evidence of life. Researchers improved transit observations in 2002, opening an exciting window into a new world.
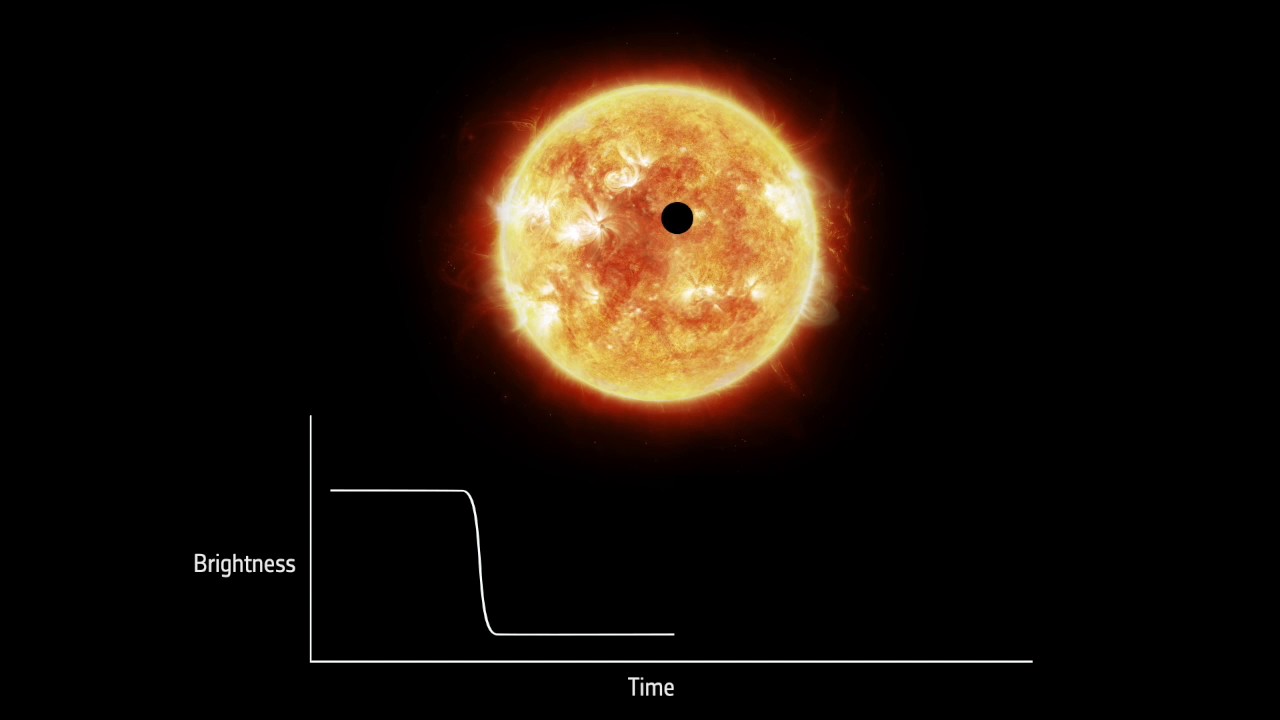
watch on
For a while, it seemed to be working perfectly. But starting in 2007, astronomers noticed that sunspots on stars – cool, active regions of the star – could interfere with transit measurements.
In 2018 and 2019, he received his then-Ph.D. student Benjamin V. Lacombe, astrophysicist Mark Giampapa, and I published a series of studies showing how fainter starspots and brighter, magnetically active stellar regions can seriously mislead measurements of exoplanets. We named this problem the “passing light effect.”
Most stars are spotted, active, and continually changing. Ben, Mark, and I showed that these changes change the signal from the exoplanet. To make matters worse, some stars also have water vapor present in their upper layers, and it is often more pronounced in sunspots than on the outside of the star. This and other gases can confuse astronomers who think they’ve discovered water vapor on Earth.
In our paper, published three years before the James Webb Space Telescope’s 2021 launch, we predicted that the Webb Space Telescope would not reach its full potential. We sounded the alarm. Astronomers have noticed that we try to judge wine by flickering, erratic candlelight.

Birth of Pandora
For me, Pandora started with an interesting email from NASA in 2018. Elisa Quintana and Tom Barclay, two prominent scientists from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, asked for a chat. They had an unusual plan. They wanted to build a space telescope very quickly to help tackle star pollution in time to assist Webb. This was an exciting idea, but also very challenging. Space telescopes are very complex and are not usually built in a hurry.
you may like
Pandora breaks NASA’s traditional model. We proposed and built Pandora more quickly and at significantly lower cost than typical NASA missions. Our approach meant keeping the mission simple and accepting a slightly higher risk.
What makes Pandora special?
Because Pandora is small, she cannot gather as much light as her older brother, Webb. But Pandora will do something that Webb cannot. By patiently observing stars, we will be able to understand how their complex atmospheres change.
By looking at stars 24 hours a day with visible and infrared cameras, we will measure subtle changes in star brightness and color. As active regions of stars rotate into and out of view, and as star points form, evolve, and disappear, Pandora records them. While Webb rarely returns to the same planet with the same equipment configuration and rarely monitors its host star, Pandora revisits its target star 10 times a year, spending more than 200 hours on each.
With that information, our Pandora team will be able to figure out how changes in the star affect observed planetary transits. Like Webb, Pandora will also observe planetary transit phenomena. By combining data from Pandora and the Web, our team will be able to better understand what exoplanet atmospheres are made of.
After a successful launch, Pandora now orbits the Earth approximately every 90 minutes. Pandora’s systems and features are currently being thoroughly tested by Pandora’s primary builder, Blue Canyon Technologies.
About a week after liftoff, control of the spacecraft will be transferred to the University of Arizona’s Multi-Mission Operations Center in Tucson, Arizona. Then, our scientific team’s research will begin in earnest and we will begin to capture starlight filtered through the atmospheres of other worlds and see them with new, stable eyes.
Source link

